doi: 10.56294/sctconf2024.1135
Category: Finance, Business, Management, Economics and Accounting
ORIGINAL
Managing tourism development: deploying successful strategies and techniques
Gestión del desarrollo turístico: aplicación de estrategias y técnicas eficaces
Oleksii Albeshchenko1 ![]() *, Olha Pryhara2
*, Olha Pryhara2 ![]() , Inha Krupenna3
, Inha Krupenna3 ![]() , Iryna Budnikevich3
, Iryna Budnikevich3 ![]() , Olena Shevchenko4
, Olena Shevchenko4 ![]()
1Mykolayiv National Agrarian University, Department of Economic Cybernetics and Mathematical Modeling, Mykolayiv, Ukraine.
2Uzhhorod National University, Faculty of Tourism and International Communications, Tourism Department, Uzhhorod, Ukraine.
3Yuriy Fedkovych Chernivtsi National University, Faculty of Economic, Department of Marketing, Innovations and Regional Development, Chernivtsi, Ukraine.
4National Scientific Centre “Institute of Agrarian Economics”, Kyiv, Ukraine.
Cite as: Albeshchenko O, Pryhara O, Krupenna I, Shevchenko O. Managing tourism development: deploying successful strategies and techniques. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias. 2024;3:.1135. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2024.1135
Submitted: 07-02-2024 Revised: 05-05-2024 Accepted: 19-08-2024 Published: 20-08-2024
Editor: Dr.
William Castillo-González ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the tourism sector is gaining importance every year within the economies of individual countries and globally. Even the largest economies in the world, such as the United States of America and the People’s Republic of China, include a significant portion of their income from tourism. The coronavirus pandemic somewhat halted tourism development; however, our study sector is beginning its new development trajectory today. Therefore, the issue of finding ways to implement effective strategies and tools for tourism development is relevant and requires scientific resolution.
Objective: the study aims to scientifically substantiate ways to implement effective strategies and determine tools for their practical implementation in tourism development management.
Method: based on the analysis of statistical data and forecasted indicators, the study identifies the importance and role of the tourism sector in developing individual state economies and the global economy.
Results: the most effective strategies for tourism management are marketing strategies. Key strategies include: overall marketing strategies for specific regions, strategies by tourism type, and those combining regions and tourism types. Additionally, strategies for specific accommodation locations and country-specific strategies by tourist type are recommended. Tools enhancing these strategies include branding, content marketing, live video marketing, electronic marketing, and experiential marketing.
Conclusions: exciting and promising topics for further research on the issue include continuing to substantiate a broader range of tools that can be applied in tourism management and finding new ways to improve the tourism sector.
Keywords: Tourism; Tourism Development Management; Tourism Marketing Strategies; Marketing Tools; Branding of Tourist Areas; Tourist Regions.
RESUMEN
Introducción: el sector turístico está ganando importancia cada año dentro de las economías de los países individuales y a nivel mundial. Incluso las economías más grandes del mundo, como los Estados Unidos de América y la República Popular China, incluyen una parte significativa de sus ingresos del turismo. La pandemia del coronavirus detuvo un poco el desarrollo del turismo; sin embargo, nuestro sector de estudio está comenzando hoy su nueva trayectoria de desarrollo. Por lo tanto, la cuestión de encontrar formas de implementar estrategias y herramientas efectivas para el desarrollo del turismo es relevante y requiere una resolución científica.
Objetivo: el estudio tiene como objetivo fundamentar científicamente las formas de implementar estrategias efectivas y determinar herramientas para su implementación práctica en la gestión del desarrollo turístico.
Método: con base en el análisis de datos estadísticos e indicadores previstos, el estudio identifica la importancia y el papel del sector turístico en el desarrollo de las economías de los estados individuales y la economía global.
Resultados: las estrategias más efectivas para la gestión del turismo son las estrategias de marketing. Las estrategias clave incluyen: estrategias de marketing generales para regiones específicas, estrategias por tipo de turismo y aquellas que combinan regiones y tipos de turismo. Además, se recomiendan estrategias para ubicaciones de alojamiento específicas y estrategias específicas de cada país por tipo de turista. Las herramientas que mejoran estas estrategias incluyen la creación de marca, el marketing de contenidos, el marketing de vídeo en directo, el marketing electrónico y el marketing experiencial.
Conclusiones: entre los temas interesantes y prometedores para futuras investigaciones sobre el tema se encuentran la búsqueda de una gama más amplia de herramientas que se puedan aplicar en la gestión del turismo y la búsqueda de nuevas formas de mejorar el sector turístico.
Palabras clave: Turismo; Gestión del Desarrollo Turístico; Estrategias de Marketing; Herramientas de Marketing; Branding de Zonas Turísticas; Regiones Turísticas.
INTRODUCTION
Tourism is one of the most dynamically developing sectors of the economy today. Despite all the challenges tourism faces, such as political instability, terrorist acts, natural disasters, and health crises, including the COVID-19 pandemic, it continues to proliferate.(1) Every year, in many countries, the revenue generated from the tourism sector is a significant component of the gross domestic product (GDP).
Bloomberg, citing a forecast by the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), writes that the volume of global revenue from the tourism sector will increase by 50 % by 2034 compared to 2019, reaching 15,5 trillion dollars, which will account for approximately 11,6 % of the global GDP.(2)
The importance of the tourism sector for the European Union is worth noting. The World Tourism Organization (WTO) notes that European countries are a priority tourist destination globally, accounting for about 50 % of the entire market. Today, thanks to the tourism industry, the overall GDP receives 10,2 % of its size (2021). According to the organisation’s forecast, the “tourism GDP” of the European Union is expected to grow to 11,2 % by 2027.(3)
Among the open data of European countries regarding their GDP composition and size, Croatia (11 %), Portugal (8 %), Spain (7 %), Italy (6 %), and Austria (5 %) have the highest share of tourism in the overall GDP(4) (figure 1).
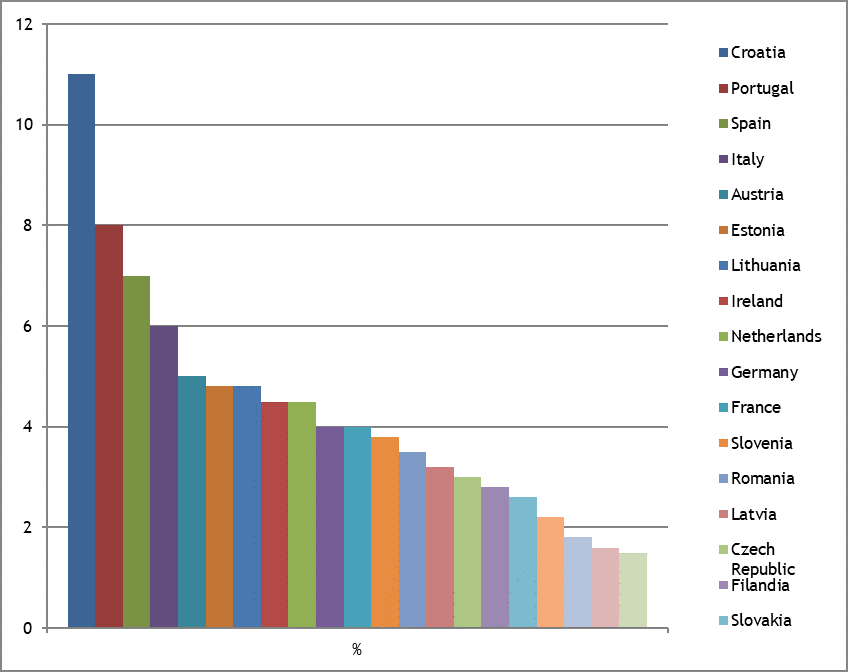
Figure 1. Share of Tourism in the Total GDP of European Countries
Sources: European Commission(5)
By approximating the given data, we can see that the tourism sector in European countries is one of the trending sectors of the economy, with an average impact on GDP amounting to 4,5 % of the country’s GDP (figure 2).
The tourism sector is an essential component of the economies of individual countries, particularly for one of the most dynamic economies - the People’s Republic of China. According to the World Travel and Tourism Council, by 2033, the share of tourism in the Chinese economy will reach 14,1 %, amounting to 4 trillion dollars. Thus, China could surpass the long-term leader in this field - the USA, where the share of income from the tourism sector will be 10,1 % of the entire economy, equivalent to 3 trillion dollars.(2)
Given the above, it can be asserted that the potential of the tourism industry is growing and becoming increasingly significant worldwide, which, in turn, drives the economic share of tourism to increase in both developed and developing countries.(5)
Figure 2. Average Share of Tourism in GDP of European Countries
Sources: European Commission(5)
The provided data indicates the importance of the tourism sector for individual countries and the global economy. However, socio-political crises occurring worldwide, such as the pandemic due to the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, create obstacles to the further development of the global tourism sector. Therefore, the issue of tourism development management is relevant and requires scientific resolution, particularly the theoretical justification of possible ways to implement effective strategies and tools.
The issue of tourism development is relevant and constantly present in scientific discourse. There are several approaches to identifying tools for developing the tourism sector. According to researchers, such tools may include analytical tools for tourism development using social media data and spatial morphological analysis;(6) tools related to the use of technological innovations;(7) Metaverse technologies;(8) virtual reality technologies that allow potential tourists to “try before they buy,”(9) and others.
Significant attention among scientists is given to marketing strategies for tourism development,(10) as the development of such a strategy serves as a primary tool for implementing marketing planning of specific actions, the execution of which can create entire areas capable of attracting visitors, considering the specific features of the area. Positive results from the application of marketing technologies are demonstrated by the experiences of countries such as Vietnam and South Africa, which, as a result of their use, have achieved economic prosperity, improved social welfare, and preserved their cultural and natural heritage.(11)
At the same time, it is worth noting that considering the development of the tourism sector, it should be remembered that it inevitably leads to an increase in the number of visitors, impacts on the environment, and generally affects the lives of residents. Considering these factors, it is essential to study the opinions of residents of regions regarding such development and the transformations that occur in them. This topic is the focus of studies examining the attitudes of regional residents towards tourism development, including types such as rural tourism,(12) medical tourism,(13) and mountain tourism.(14)
Every year, the issue of over-tourism arises, meaning the excessive growth of tourism in certain regions, which creates social(15) and economic impacts on the environment. Such impacts include the touristification of public places, overpopulation, and increased living costs that negatively affect residents’ quality of life.(14) Regarding environmental impacts, researchers have highlighted carbon impacts on tourist sites (many vehicles) and increased pressure on biodiversity and ecosystems, which are vulnerable to climate change.
In their studies, many scientists consider tourism development through the lens of destination and emphasise the diversity of this process by region.(16) This statement is confirmed in the study,(17) where it is noted that destination positively contributes to greater market sustainability of tourism services.
It is also worth noting that practical cooperation among all stakeholders in the tourism sector contributes to its development, as cooperation ensures creativity and innovation. Technological interdependence requires joint innovations in products and processes.
The main aim of the presented article is to theoretically substantiate the ways of implementing effective strategies and tools in tourism development management and to develop practical recommendations for their realisation.
METHOD
The research materials include 1) statistical data and forecast indicators from international organisations operating in the tourism sector, namely the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) and the World Tourism Organization (WTO), and 2) the creative contributions of researchers who conducted their studies in the field of tourism development.
The research’s methodological basis comprises a system of general scientific and unique methods. The integrity of the scientific research was ensured through systematic and comprehensive approaches, which allowed for a theoretical analysis of possible ways to implement effective strategies and tools in tourism development management.
The collection of scientific information on the chosen research topic was made through a comprehensive and systematic analysis of scientific sources and statistical and analytical reports. To achieve the set research goal, the following methods were applied: the method of comprehensive analysis to determine the role of the tourism sector in the economies of individual countries and globally; methods of induction and deduction – for identifying effective strategies and tools in tourism development management; the method of comparison to highlight the advantages of some tourism development tools over others; methods of abstraction were used to specify tourism development strategies and tools; the method of logical generalisation of results to formulate conclusions.
RESULTS
2024 is expected to be a year of tourism growth worldwide, with tourism projected to increase by more than a third compared to 2023 and previous years.(18) (figure 3)
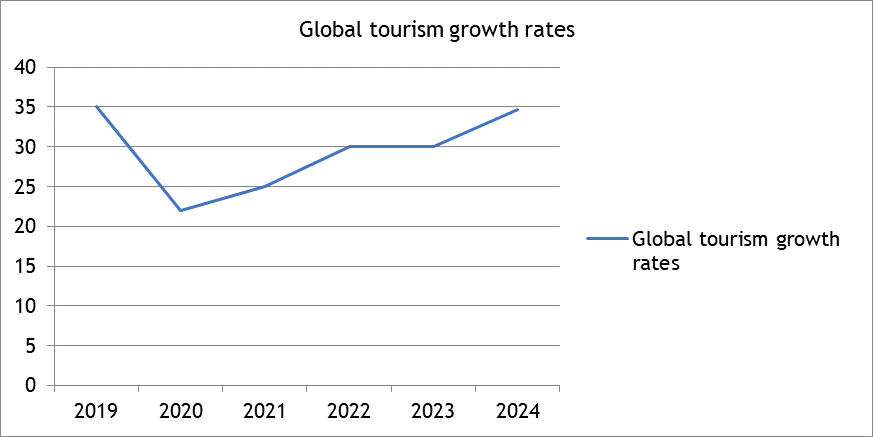
Figure 3. Growth Rate of World Tourism in 2024 compared to previous years
Sources: WP Travel(18)
The increase in tourism growth is a process directly related to the management of tourism development itself. Tourism development management in each country varies in its organizational structure and tasks. Sometimes, even within one country, tourism development differs depending on its region. However, regardless of the structure and tasks of tourism development in a particular country or region, an essential element remains the determination of strategic directions through effective strategies and tools.
As the practical field of tourism shows, marketing strategies have become effective strategies in this area. The issue of developing territories through marketing strategies has gained importance over the past decades.
Marketing strategies that are effective and can be applied in the process of tourism development management can be divided into the following types:
1. General tourism marketing strategy in a precisely defined administrative-territorial unit and its detailing by types of tourism. This strategy focuses on providing general information about tourism in a particular administrative-territorial unit and, if this region has an internal territorial division, further highlighting the information by internal units. The main advantage of this strategy is the use of coordinated tourism marketing by the regional authorities and its territories. This strategy also fosters the development of the region’s tourist potential. An example of the effective implementation of this strategy is the state of Hawaii in the USA.
2. Tourism-type marketing strategy. This strategy focuses on presenting information by types of tourism. Specifically, many tourism types are highlighted, such as mountain tourism, medical tourism, boating, and marine recreation. Each selected direction is assigned to a responsible expert or a group of experts who work on its development. The advantages of this strategy include considering all possible development options for a particular type of tourism and making it the visiting card of a specific country or region. A positive example of this strategy’s application is the state of Florida in the USA, known worldwide for its beach vacations.
3. Marketing strategy combining regions and types of tourism. The features of choosing and implementing this marketing strategy lie in the fact that potential clients first choose the type of tourism they are interested in and then the region where the selected type of tourism is available. Alternatively, they may choose the region and the type of tourism developed there. An example of the successful application of this strategy is the state of Texas in the USA.
4. Marketing strategy for specific locations of tourist sites. This strategy focuses on the development of less known and less famous regions. Maximum efforts are made to advertise these regions, mainly by including brochures of various types of tourism at the regional or national level. At the same time, these territories themselves make efforts to promote themselves in the tourism market. The advantages of this strategy include developing little-known areas and balancing the development level of the tourism sector across all regions. This practice has been successfully applied and has shown its effectiveness in the United Kingdom.
5. Marketing strategy by types of tourism and tourists across countries. Similar to the strategy by types of tourism, this strategy focuses on presenting information by types of tourism. Many types of tourism, such as mountain, medical, boating, and marine recreation, are highlighted. However, this strategy considers the characteristics of potential tourists, including language, religious, economic, and other aspects. The advantages of this strategy are that each tourist can be in an environment that considers their linguistic, religious, economic, and other characteristics. Such strategies are common in the federal states of Berlin and Bavaria in Germany.
The implementation of a particular strategy and the results obtained from it depend on the correctly chosen tools. It is crucial to consider the tools for tourism development. Based on researchers’ opinions in this field, existing statistical materials, and the practical experience of individual regions and countries, we believe that the following tools can be used:
1. Branding. Branding of territories is an essential element of modern tourism development strategies. It aims to develop, increase competitiveness, improve the socio-cultural state of various regions, and stimulate tourist and hospitality institutions in different localities.
Branding makes it possible to draw attention to a specific territory by potential clients of tourism services and investors. Branding for tourist regions should focus on the following aspects: identifying and ensuring the effective presentation of the region’s attractiveness through integrated communication tools and improving loyalty among the target audience. The centre of the tourism brand of a particular region can be famous natural, cultural-historical sites or entire complexes, as well as individual tourist routes or unique events associated with these sites that attract many visitors. Thus, the foundation is formed to create a tourism product for a particular region or country.
The essence of territory branding manifests in strategically promoting a specific territory (country, city, region) to attract tourists, increase investment attractiveness, and improve competitiveness in global rankings. The branding tool allows for forming a unique image of the territory, distinguishing it from others as unique and individual.
The advantages of applying a tourism brand are rational-functional and emotional-value aspects. The first category focuses on the advantages of the tourism service (e.g., the ecological aspects of the region and its infrastructure) and their comfortable use. The second category reflects the emotional experience of the visitor during interaction with the brand and the values associated with the region and its tourism product.
2. Content Marketing. Content marketing is a technology that attracts attention and engages the target audience with a brand by creating and disseminating relevant information. The foundation of content marketing consists of two concepts: “content” and “marketing.” The first concept relates to information, and the second promotes this information among potential clients. In this regard, content marketing aims to disseminate information through various channels to provide certain services or products or to attract visitors.
Today, powerful channels for content marketing are websites and social media. A well-developed content plan is a crucial factor in reaching potential tourists. This tool can emphasise the authenticity of a specific territory and highlight its exciting aspects.
The advantages of using content marketing in the tourism sector include increasing the recognition of a specific tourist region or country, improving the reputation of all stakeholders in the tourism sector, providing a wide range of audience coverage, maintaining the tourist’s attention for a long time, creating trustful relationships with potential or actual clients, stimulating visits to the region, and ensuring a long-term effect from using this tool.
3. Live Video Marketing. Live video marketing in the tourism sector involves using live video broadcasts to showcase tourist attractions, routes to them, and unique rituals of a particular region or country. In other words, this tool can be described as a virtual tour in real-time, allowing viewers to see hotel rooms, famous architectural landmarks, and more.
Based on statements from renowned marketing experts on video marketing, the following trends are dominant in this type of marketing: video is increasingly replacing other forms of communication; video will continue to grow, concise and vertical videos; tools for creating videos are expanding, making video editing easier; personalised and authentic videos are becoming a trend. All these trends are significant when using video marketing in the tourism sector.
This tool allows tourists to experience their future vacation spots, encouraging them to choose this place for their travels. The undeniable advantages of using live video marketing are the ability to quickly and easily provide information about a tourist region to any point in the world, as well as the fact that video information is convenient and accessible for perception.
4. Electronic Marketing. This tool involves creating a mailing list by strategically integrating data obtained through registration forms on the website. Electronic marketing lets you provide information about your tourist area and its authenticity and notify potential clients about promotions, discounts, or guides, which helps form a pool of interested potential clients.
When using electronic marketing in the tourism sector, it is advisable to use the following types of emails: special offers and promotions, travel guides and tips, event updates, personalised recommendations according to the needs of specific target audiences, and follow-up information after a visit.
The advantages of using electronic marketing tools in tourism development management include directly connecting with potential clients.
5. Experience Marketing Concept. Adopting this concept changes how your target audience perceives your brand. Experiential marketing, also known as engagement marketing, is a strategy that focuses on creating exciting and enjoyable experiences for tourists.
This tool involves promoting your tourist area and engaging the audience deeper by leaving a memorable impression beyond the transaction.
Critical ideas for implementing experiential marketing in the tourism sector include creating themed events that showcase the uniqueness and authenticity of your tourist region; collaborating with local artisans through exhibitions and workshops that emphasise the authenticity and uniqueness of your region; conducting interactive tours; offering culinary experiences through gastronomic tours, cooking classes, or unique dishes that promote local cuisine, creating a sensory journey for tourists. (19)
An exciting and successful example of experiential marketing is Airbnb’s campaign, which allowed visitors to have positive experiences by spending time in iconic places, such as a night at the Louvre or Dracula’s Castle.
6. Artificial Intelligence Technologies. AI technologies evolve and become integral to effective and efficient marketing strategies. Using live chatbots in customer service improves client interactions and provides instant responses to inquiries.
The advantages of using AI technologies include convenience and efficiency, which enhance interaction with tourists. Additionally, this tool can increase productivity and efficiency in the tourism sector, reduce human errors, and ensure efficiency in repetitive tasks.
The provided list can be supplemented with other tools. However, when determining the feasibility of implementing such tools, it is essential to remember that they must be innovative, accessible anywhere in the world, reach the maximum possible number of potential clients, and be user-friendly, among other considerations.
Considering the given data and justifications for the potential implementation of effective strategies and tools in tourism management, we can predict that the tourism sector will proliferate over the next decade. Specifically, the growth rate of tourism could exceed economies’ growth rates. Additionally, this tourism growth will increase its role in the global GDP, and it can be forecasted that in a decade, it will be even higher than the forecasts by the World Travel and Tourism Council, fluctuating around 15 per cent. Among the leaders in the tourism sector, the current situation is expected to remain, with the leaders being the United States of America, the People’s Republic of China, Germany, the United Kingdom, Japan, France, Mexico, Italy, India, and Spain. However, considering the economic growth rates of the People’s Republic of China, it can be predicted to take the lead in this ranking.
DISCUSSION
The obtained results indicate the achievement of the research objective. In particular, the theoretical possibility of implementing the following marketing strategies has been substantiated: a general tourism marketing strategy in a precisely defined administrative-territorial unit and its detailing by types of tourism; a marketing strategy by types of tourism; a marketing strategy combining regions and types of tourism; a marketing strategy for specific locations of tourist sites; and a marketing strategy by types of tourism and tourists across countries. Additionally, tools have been identified whose application in tourism development management will facilitate the implementation of these strategies and enhance their effectiveness, namely branding, content marketing, live video marketing, electronic marketing, and experiential marketing.(20)
The results are a foundation for public administration bodies to create a regulatory framework and practical steps for managing tourism development in a specific region or country. Furthermore, the mentioned strategies can be used by local authorities to develop their tourist destinations. Stakeholders in the tourism sector can use this research to improve their economic activities in the tourism sphere, mainly by applying the identified tourism development tools.
CONCLUSIONS
The article presents a theoretical study of a current scientific topic, which involves the theoretical substantiation of ways to implement effective strategies and tools in tourism development management and the development of practical recommendations for their implementation. The research results indicate that the tourism industry has overcome the consequences of the pandemic related to the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection and is now in a new development stage.
Despite travel restrictions worldwide and other pandemic measures, the tourism industry has been. It remains an essential component of the economies of individual countries, including leading world economies like the United States of America and the People’s Republic of China. It constitutes a significant part of the global gross domestic product.
To ensure further tourism development, it is necessary to manage it effectively. One of the effective methods for managing such development is the implementation of effective strategies and tools. According to practical indicators, the most effective strategies are marketing strategies, particularly the general tourism marketing strategy in a precisely defined administrative-territorial unit and its detailing by types of tourism; marketing strategy by types of tourism; marketing strategy combining regions and types of tourism; marketing strategy for specific locations of tourist sites; and marketing strategy by types of tourism and tourists across countries.
Such strategies will positively impact the tourism sector and allow for developing tourist regions and various types of tourism. To ensure the effectiveness of the mentioned strategies, it is essential to apply appropriate tools that are innovative, engaging, convenient, compact, and accessible to tourists. We have substantiated that such tools may include branding, content marketing, live video marketing, electronic marketing, and the concept of experiential marketing. Exciting and promising topics for further research on the issue include continuing to substantiate a broader range of tools that can be applied in tourism management and finding new ways to improve the tourism sector.
REFERENCES
1. WTTC (World Travel and Tourism Council). Understanding the critical issues for the future of travel and tourism, March 2017. London: WTTC.
2. Bloomberg. Are you a robot? [Internet] 2023 [cited: 21/08/2023]. Available in: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-08-21/global-travel-and-tourism-will-represent-a-15-5-trillion-economy-by-2033?srnd=premium-europe
3. UNWTO (United Nations World Tourism Organization): Reports [Internet] 2020 [cited: 25/07/2024]. Available in: https://www.unwto.org/sustainable-development/reports-oneplanet-stp
4. Peters M, Pfurtscheller A, Wong K, Kraus S. The influence of entrepreneurial branding on entrepreneurial/growth orientations: an empirical study in the Austrian tourism industry. International Journal of Business Research 2010; 10(2): 28-29.
5. European Commission. Tourism: €572 billion gross value added in the EU. Language selection [Internet] 2023 [cited: 14/04/2023]. Available in: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-eurostat-news/w/wdn-20230414-1
6. Suvannadabha P, Busayarat C, Supnithi T. The Analytical Tools for Tourism Development through Social Media Data and Spatial Morphological Analysis. Nakhara: Journal of Environmental Design and Planning [Internet] 2022 [cited: 27/12/2022]; 21(3): Article 223. Available in: https://doi.org/10.54028/NJ202221223
7. Ferraris A, Belyaeva Z, Bresciani S. The role of universities in the smart city innovation: multistakeholder integration and engagement perspectives. Journal of Business Research [Internet] 2020 [cited: 25/11/2020]; 119: 163-171. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.12.010
8. Gursoy D, Malodia S, Dhir A. The metaverse in the hospitality and tourism industry: an overview of current trends and future research directions. J Hosp Mark Manag [Internet] 2022 [cited: 03/05/2022]; 31(5): 527-534. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2022.2072504
9. Bogicevic V, Seo S, Kandampully JA et al. Virtual reality presence as a preamble of tourism experience: the role of mental imagery. Tour Manag [Internet] 2019 [cited: 06/03/2019]; 74: 55-64. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.02.009
10. MiorSharifuddin NS, Azinuddin M, Hanafah MH et al. A comprehensive review of tourism destination competitiveness (tdc) literature. Compet Rev Int Bus J [Internet] 2023 [cited: 01/06/2023]; 33(4): 787-819. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1108/CR-04-2021-0054
11. Zhao Zh. Tourism Development and Marketing Strategies in Emerging Markets. Tourism Management and Technology Economy [Internet] 2023 [cited: 09/11/2023]; 6(7): 26-32. Available in: http://doi.org/10.23977/tmte.2023.060704
12. Wu MY, Wu X, Li QC, Tong Y. Community citizenship behaviour in rural tourism destinations: Scale development and validation. Tourism Management [Internet] 2022 [cited: 24/11/2021]; 89: Article 104457. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104457
13. Suess C, Baloglu S, Busser J. Perceived impacts of medical tourism development on community wellbeing. Tourism Management [Internet] 2018 [cited: 23/06/2018]; (69): 232-245. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.06.006
14. Ali A. Residents’ attitude and perception toward the impact of mountain tourism in Gilgit-Baltistan Pakistan. Journal of Public Affairs [Internet] 2022 [cited: 14/12/2020]; 22(3): Article e2577. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2577
15. Clancy M. Overtourism and resistance. In Overtourism – Tourism Management and Solutions. Edited by Herald Pechlaner, Elisa Innerhofer and Greta Erschbamer. Oxon: Routledge [Internet] 2020 [cited: 25/07/2024]; 14-24. Available in: https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429197987-2
16. Calero C, Turner L. Regional economic development and tourism: A literature review to highlight future directions for regional tourism research. Tourism Economics [Internet] 2020 [cited: 18/10/2019]; 26(1): 3-26. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1177/1354816619881244
17. Elvekrok I, Vefen N, Scholderer J, Sørensen BT. Effects of network relations on destination development and business results. Tourism Management [Internet] 2022 [cited: 29/07/2021]; 88: Article 104402. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104402
18. WP Travel. Global Tourism Statistics 2024: Facts and Forecasts [Internet] 2024 [cited: 25/07/2024]. Available in: https://wptravel.io/global-tourism-industry-statistics/#h-global-tourism-statistics-2024-predictive-analysis
19. El Chaarani H, Raimi L. Diversity, entrepreneurial innovation, and performance of the healthcare sector in the COVID-19 pandemic period. Journal of Public Affairs [Internet] 2022 [cited: 04/01/2022]; 22(S1): 2-28. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2808
20. Holden A, Tazim J, Federica B. The Future of Tourism in the Anthropocene. The Annual Review of Environment and Resources [Internet] 2022 [cited: 26/07/2022]; 47: 423-47. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-120920-092529
FINANCING
The authors did not receive funding for the development of this research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara, I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.
Data curation: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara.
Formal analysis: I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.
Research: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara, I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.
Methodology: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara, I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.
Project management: O. Albeshchenko.
Resources: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara, I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.
Software: O. Pryhara.
Supervision: Krupenna.
Validation: I. Budnikevich.
Display: O. Shevchenko.
Drafting – original draft: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara, I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.
Writing – proofreading and editing: O. Albeshchenko, O. Pryhara, I. Krupenna, I. Budnikevich, O. Shevchenko.