doi: 10.56294/sctconf2024.1205
ORIGINAL
The role of ChatGPT on academic research: perspectives from filipino students across diverse educational levels
El papel de ChatGPT en la investigación académica: perspectivas de estudiantes filipinos en diversos niveles educativos
Jomar C. Cabuquin1
![]() *,
Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre1
*,
Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre1
![]() , Mary Ann A. Manabat1
, Mary Ann A. Manabat1
![]() , Mary Grace H. Aruta2
, Mary Grace H. Aruta2
![]() , Julinito Sangutan3
, Julinito Sangutan3
![]() , Romer F. Beltran Yu4
, Romer F. Beltran Yu4
![]()
1Eastern Visayas State University, Science and Mathematics Education Department. Tacloban City 6500, Leyte, Philippines.
2Eastern Visayas State University, Elementary Education Department. Tacloban City 6500, Leyte, Philippines.
3Eastern Visayas State University, Technical-Vocational Education Department. Tacloban City 6500, Leyte, Philippines.
4Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges, College of Arts and Sciences. Camarines Sur 4434, Bicol, Philippines.
Cite as: Cabuquin JC, Sandra Acidre MA, Manabat MAA, H. Aruta MG, Sangutan J, Beltran Yu RF. The role of ChatGPT on academic research: perspectives from filipino students across diverse educational levels. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias. 2024; 3:.1205. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2024.1205
Submitted: 17-03-2024 Revised: 18-06-2024 Accepted: 20-10-2024 Published: 21-10-2024
Editor: Dr.
William Castillo-González ![]()
Corresponding author: Jomar C. Cabuquin *
ABSTRACT
With the emergence of technology, artificial intelligence (AI) is introducing a new wave of remarkable tools and transformations in education. One such technological development is ChatGPT, a dialogue system designed to collect and organize information, which is then converted into text-based inputs to address user inquiries. There is also a clear trend in which many Filipino students increasingly use ChatGPT for academic research. Filipino students’ growing usage of ChatGPT demands immediate attention to examine its role in academic research within the Philippine educational setting. Thus, this study examines how ChatGPT is used in academic research by exploring students’ perspectives and analyzing its perceived benefits and challenges. A descriptive cross-sectional design was conducted in the Eastern Visayas region of the Philippines, explicitly targeting selected secondary and tertiary schools. A total of 316 students were involved in the study, selected through convenience sampling. Results revealed ChatGPT to be moderately useful for various aspects of academic research and moderately influential in the student’s academic performance. Receiving additional information or resources, getting help with mechanics, writing, paraphrasing, and generating ideas were found to be the benefits of using ChatGPT. Nonetheless, students commonly encountered issues such as redundant, inadequate, and inaccurate information provided by ChatGPT and concerns regarding its accessibility and the potential for plagiarism. To optimize advantages and address possible concerns, academic institutions should establish concise guidelines and regulations for responsible student utilization of ChatGPT.
Keywords: Academic Research; ChatGPT; Cross-sectional Design; Filipino Students; Perspectives.
RESUMEN
Con el surgimiento de la tecnología, la inteligencia artificial (IA) está introduciendo una nueva ola de herramientas y transformaciones notables en la educación. Uno de esos avances tecnológicos es ChatGPT, un sistema de diálogo diseñado para recopilar y organizar información, que luego se convierte en entradas basadas en texto para atender las consultas de los usuarios. También existe una clara tendencia en la que muchos estudiantes filipinos utilizan cada vez más ChatGPT para investigaciones académicas. El creciente uso de ChatGPT por parte de los estudiantes filipinos exige atención inmediata para examinar su papel en la investigación académica dentro del entorno educativo filipino. Por lo tanto, este estudio examina cómo se utiliza ChatGPT en la investigación académica explorando las perspectivas de los estudiantes y analizando sus beneficios y desafíos percibidos. Se llevó a cabo un diseño transversal descriptivo en la región de Visayas Oriental de Filipinas, dirigido explícitamente a escuelas secundarias y terciarias seleccionadas. En el estudio participaron un total de 316 estudiantes, seleccionados mediante muestreo por conveniencia. Los resultados revelaron que ChatGPT es moderadamente útil para diversos aspectos de la investigación académica y moderadamente influyente en el rendimiento académico del estudiante. Se descubrió que recibir información o recursos adicionales, obtener ayuda con la mecánica, escribir, parafrasear y generar ideas son los beneficios de usar ChatGPT. No obstante, los estudiantes comúnmente encontraron problemas como información redundante, inadecuada e inexacta proporcionada por ChatGPT y preocupaciones sobre su accesibilidad y el potencial de plagio. Para optimizar las ventajas y abordar posibles inquietudes, las instituciones académicas deben establecer pautas y regulaciones concisas para el uso responsable de ChatGPT por parte de los estudiantes.
Palabras clave: Investigación Académica; ChatGPT; Diseño Transversal; estudiantes filipinos; Perspectivas.
INTRODUCTION
The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) in education has gained significant attention in many different fields of study, including academic research.(1) As individuals search for knowledge, many use AI tools to increase their creative abilities and accelerate research. Among these AI technologies, ChatGPT has received much attention as a powerful tool transforming the landscape of academic inquiry and creating new opportunities for exploration and discovery.(2) ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) is an OpenAI language model that generates human-like text depending on user input(3) and enables interactive discussions. While there is existing literature on the impact of AI on research practices, there is a need to have more studies on the specific role of ChatGPT from the perspective of students at different levels of education.
Previous studies(4,5,6) have reported that ChatGPT is proficient at answering frequently asked questions, even those requiring coding skills. However, users need to acknowledge that while ChatGPT makes getting answers or information easier, concerns about its impact on student motivation to do independent research exist. One primary concern is that student researchers will rely too much on ChatGPT for their writing needs and outsource research writing. Lee and Soylu(7) emphasized the necessity to explore alternative ways to teach research skills and assess students’ deep, critical, and sophisticated thinking. In this way, students would only rely a little on ChatGPT at the expense of developing their critical thinking skills, which are essential for academic research.
Furthermore, ChatGPT can boost research efficiency, productivity, and quality in academic settings. It can quickly process vast amounts of data to extract insights and identify information. ChatGPT allows students to focus on critical thinking and analysis by automating tasks like data preprocessing and literature review. Moreover, ChatGPT is interactive to provide real-time suggestions and feedback. Nevertheless, Firat(8) pointed out that the integration of ChatGPT in education also raises questions about the challenges and obstacles that will arise from this technological shift. Rasul et al.(9) further stressed the ethical utilization of ChatGPT in education because of the potential misuse of this AI tool among students.
In the Philippine setting, there is an evident pattern in which many students are using ChatGPT more frequently as a tool for their academic research projects. Filipino students’ increased use of ChatGPT calls for immediate attention to study its role in scholarly research within the Philippine educational setting. Furthermore, there remains a gap in the literature that deals with ChatGPT in academic research, especially from the standpoint of students across diverse levels of education. While some studies in this field have been conducted, it is essential to note that the specific lens of understanding how students at diverse educational levels perceive and utilize ChatGPT in academic research has yet to be thoroughly explored in the Philippine context. As a result, this study aims to shed light on this evolving phenomenon and provide significant insights into the implications of ChatGPT among students.
Considering the rationale presented, this study generally aimed to examine the role of ChatGPT in academic research by examining Filipino students’ perspectives across diverse educational levels. Specifically, this study assessed (1) the extent to which students at diverse educational levels utilize and perceive the role of ChatGPT as a tool for academic research and (2) the perceived benefits and challenges associated with using ChatGPT in academic research among students. The study argued that grasping how students view and use ChatGPT in academic research could assist teachers and school officials make informed decisions about integrating AI tools in educational settings. Furthermore, this study contributes to the existing literature by documenting how the tool’s evolving capabilities impact students’ academic research practices.
Literature review
ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) represents an AI-powered framework for content generation, attracting global recognition for its adeptness in handling intricate language comprehension and production endeavors within conversational contexts.(10) Its emergence has stimulated advancements in several fields, and its extraordinary capabilities have been among the most talked-about topics lately in education. With a single click, it swiftly creates and offers extensive information. It provides numerous benefits, including assessment innovation, instructional support, remote learning, research design, academic writing support, and administrative assistance.(11) ChatGPT and its derivatives would revolutionize education.(12)
The progress of ChatGPT rapidly gained recognition for its proficiency in providing detailed and precise answers to questions covering various subjects.(13) It has gained attention worldwide(14) as an innovative tool for enriching learning experiences and facilitating enhanced interaction between students and teachers.(15) ChatGPT can enhance knowledge accessibility, facilitate complex and self-paced learning, and reduce instructional workload.(16) It is a significant teaching, learning, and research tool. Still, it is vital to balance its advantages with restrictions and support appropriate usage.(11,17) ChatGPT is adept at personalizing learning experiences by answering questions, providing feedback, and generating educational content and lesson plans.(18)
ChatGPT exhibits the potential for reshaping teaching and learning encounters within educational technology. AI technology, including ChatGPT, can enhance teaching and learning outcomes in education.(19) It is an up-and-coming tool for students, facilitating active engagement and cognitive progress by adjusting to their learning pace.(20) It can optimize teaching methods by providing teachers and students with valuable assistance, personalization, and interactive learning experiences.(21) The launch of ChatGPT represents a crucial moment in artificial intelligence and natural language processing. As it evolves and becomes more integrated into daily life, it is essential to acknowledge the multitude of benefits it brings alongside the challenges it presents in education.
Perceived benefits associated with the use of ChatGPT in academic research among students
Several potential advantages are present for chatbots like ChatGPT in promoting the progression of learning within academic contexts. Students benefit from ChatGPT and find it effective in academic writing because it helps save time and effort by offering efficient ways to search for relevant topics and enhances scientific language use for research purposes.(17,22,23) Academic writing among students has always been a critical aspect of their educational journey, reflecting their comprehension, analytical skills, and ability to articulate ideas effectively.(24) Academic writing constitutes a crucial aspect of students’ academic endeavors and significantly influences their learning experiences. The advent of tools such as ChatGPT marks a significant enhancement in students’ academic writing abilities, generating overwhelmingly positive perceptions of its impact and reinforcing its reliability as a writing aid.(25) ChatGPT is acknowledged as a valuable instrument that enriches academic communication, education, and research through a balanced approach.(26)
Studies on students’ positive perceptions of ChatGPT and its diverse functions are prevalent in higher education. For example, a study on students learning English as a Foreign Language (EFL) indicates that integrating AI technology such as ChatGPT results in enhanced educational outcomes.(27) Another study revealed that ChatGPT also assists in writing research proposals.(28) It also assists students in learning grammar and expanding their vocabulary.(29) In addition to the study above, it was noted that most students are aware that ChatGPT commits mistakes, but still, they trust ChatGPT’s answers and are more likely to use them in the future.(30) Furthermore, university students perceive ChatGPT to enhance the learning process, leading to its acceptance.(31) Because they see its benefits in the learning process, with this point of acknowledging the significant role of AI in writing, it concludes by stressing the importance of reflecting and integrating AI technologies, highlighting the dangers of uncritical reliance and advocating for a balanced approach to nurture students’ critical thinking and intellectual.(32,33,34)
As technology advances, it is anticipated that students will increasingly embrace its integration into their learning journeys. Apart from academic writing, students also use ChatGPT as a valuable tool for gaining insights into complex topics, solving academic challenges, and accessing information, thereby enhancing their learning experiences and academic performance.(35) Students also perceived ChatGPT as a tool capable of generating customized content and providing personalized assessments, facilitating a more individualized learning approach.(36) Students adopt diverse digital tools and applications to augment their academic achievements and facilitate their educational progression. However, it is essential to emphasize that despite these advantages, ChatGPT should be utilized only under the guidance and expertise of educators.(37,38) Students should use the tool effectively and responsibly, maximizing its potential for enhancing learning outcomes.
Perceived Challenges and Limitations associated with the use of ChatGPT in academic research among students
AI technology such as ChatGPT offers promising opportunities for enhancing productivity and efficiency but also exhibits challenges and limitations that require thorough examination. Several studies specifically identify challenges and constraints in utilizing ChatGPT, including issues related to academic integrity(9,33,39), privacy and security concerns(40,41), bias, reliability issues, and factual inaccuracies(12,16,23,42,43), authenticity and plagiarism(44), unmotivated and increased dependency.(33,45) Furthermore, a study revealed potential risks in students, such as the capacity to restrict critical thinking and creativity and the tendency to cultivate laziness and passivity.(21,46,47) These challenges and limitations could negatively affect students’ academic performance and personal development.
Moreover, Sok and Heng(11) emphasized the importance of effectively utilizing ChatGPT for academic purposes among students. To mitigate and prevent potential risks, Rathod(44) suggests using these technologies cautiously, while Cotton et al.(43) and Crawford et al.(48) recommend implementing a clear policy to ensure ethical use. Additionally, Steele(49) proposes a valuable learning strategy for encouraging students to create and evaluate ChatGPT summaries of critical texts, which can enhance their comprehension skills. This will allow students to engage and deepen their understanding of the content actively. Lastly, conducting more research and investigation to understand ChatGPT’s capabilities is highly recommended thoroughly.(45) Most importantly, promoting responsible use of AI, such as ChatGPT, can ensure that students learn from it and remain critical, ethical, and informed.(50,51) With teamwork, careful planning, and implementation, ChatGPT can be a valuable tool for every student’s success.
Adoption of ChatGPT in Academic Settings
Likewise, several studies have revealed how AI and ChatGPT enhance students’ engagement and improve educational outcomes by creating personalized learning experiences.(52,53,54) The application of ChatGPT marks the revolutionary shift in how learning is delivered and embraced across different educational levels. Its flexibility facilitates the effective adoption of content from the primary to the tertiary level. It truly possesses a unique ability to create interaction and adjust the level to meet students’ individual needs and understanding.(55)
ChatGPT reinforces basic ideas in elementary education and encourages curiosity among young students by providing interactive activities, engaging content, and simplified explanations. The integration of ChatGPT offers valuable insights into its potential to improve learning outcomes.(56) Another study showed that the effectiveness of an elementary lesson plan designed using ChatGPT for teaching English was observed to achieve good validity scores, especially regarding lesson objectives and assessments.(57) A study also recognizes ChatGPT’s contribution to early childhood education as a conversational agent and support tool for educators.(58) These findings would like to emphasize the potential of ChatGPT to aid educators in the development of instructional resources, especially at the elementary level, but highlight the importance of critical evaluation of the materials.
In secondary education, ChatGPT’s ability to generate different learning activities revealed improvement in students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills.(59,60) The integration of ChatGPT can change and improve students’ education, particularly in planning and engaging with their academics.(61) It can also support students’ preparation for standardized exams(62) since ChatGPT can provide individualized learning experiences aiding with accurate prompts. Furthermore, a study showed how ChatGPT facilitates a deeper understanding of more complex scientific concepts.(63,64) ChatGPT is considered an effective support tool for teachers and students across various subjects.(65) However, it is always highly recommended that there is a need for responsible implementation, critical engagement, faculty training, and further research to maximize its educational benefits.(66)
In higher education, ChatGPT has become a very significant tool for university students, for it assists in conducting and doing research, assignments, and other school-related activities. University students’ adoption of ChatGPT stems from their impression of its potential application in learning.(31) It provides faster, real-time feedback and broader access to academic materials. It can summarize and interpret complex information for easier understanding and application in various academic tasks.(67) It can give more detailed and coherent feedback on students’ performance.(68) ChatGPT boosts learning results and makes education more accessible and exciting. Its integration into the educational system does not intend to displace human intelligence but to form a partnership, underlining the significance of these technologies’ ethical and careful deployment.(69,70)
Generally, the reviewed literature synthesizes ChatGPT as a crucial tool in the educational system, as documented in various studies. Recognizing its relevance, educators and policymakers can maintain a balance by utilizing technology to enhance education while upholding ethical principles that promote critical thinking, originality, creativity, and integrity.(71) However, there still needs to be more studies examining the long-term impacts, ethical implications, and perspectives on ChatGPT in academic research, particularly from the viewpoint of students at various educational levels. Addressing these gaps requires a wide range of research initiatives incorporating pedagogy, technology, ethics, and policymaking insights to provide comprehensive knowledge of ChatGPT’s impact across educational levels.
METHOD
Research Design
This study utilized a descriptive cross-sectional design to describe students’ perspectives on using ChatGPT in academic research and analyze the perceived benefits and challenges associated with its use. In this study, a descriptive cross-sectional design was used because it allows for collecting data from a specific population at one point in time (72,73), providing a snapshot of the respondents’ insights and perceptions on the role of ChatGPT in academic research.
Research Setting and Sampling
This study was conducted at the secondary and tertiary schools in the Eastern Visayas region, the Philippines. Using the convenience sampling technique, a total of 316 students, comprising 116 males and 200 females, responded to the survey. The respondents included students from Grades 9 to 12 and third- and fourth-year college students, as these year levels are actively involved in academic research writing. Convenience sampling was used in this study to reach a diverse group of students in the Eastern Visayas region for exploratory research on emerging technologies like ChatGPT. The study targeted students actively engaged in academic research who had used ChatGPT at least once for research purposes, particularly at the secondary and tertiary levels.
Research Instrument
The instrument used in this study was a survey questionnaire developed by the researchers to assess students’ perspectives on using ChatGPT in academic research. Similarly, relevant literature was also reviewed to inform the design of the questionnaire. The questionnaire consisted of 20 items that assessed various aspects related to ChatGPT. These included its usefulness, impact on academic performance, awareness of ethical considerations and concerns, and the likelihood of future use and recommendations. Each dimension consisted of five statements. The validity of the questionnaire was established through the review and feedback of three research teachers, whose comments and suggestions informed the refinement of the survey items. A pilot test was conducted at a non-sampled public secondary school in Leyte to ensure the instrument’s reliability. The test yielded Cronbach’s alpha (α) ≥ 0,7, indicating an acceptable internal consistency for each instrument dimension. Specifically, Cronbach’s alpha for the usefulness of ChatGPT in academic research yielded a value of 0,80, the influence of ChatGPT on academic performance (α=0,76), awareness of ethical considerations and concerns (α=0,79), and likelihood for future use and recommendations (α=0,75). Meanwhile, open-ended questions were included to gather students’ insights on the perceived benefits and challenges of using ChatGPT in academic research.
Data Gathering Procedure
Data for this study were collected during the first semester of the 2023-2024 academic year for four weeks, using an online survey questionnaire presented on Google Forms. The survey link was distributed to secondary and tertiary teachers who teach research-related subjects, requesting that they administer the survey to their students. All responses were securely stored in a Google Drive folder accessible only to the research team. The data underwent thorough examination promptly after collection.
Data Analysis
The collected data were presented in both tabular and graphical formats. Descriptive statistics, including frequency counts, means, and standard deviations, were employed to describe students’ perspectives on using ChatGPT in academic research and to analyze the perceived benefits and challenges associated with its use. Data processing and analysis were conducted using MS Excel.
Ethical Considerations
Informed consent was obtained from all respondents, and the nature and purpose of the study were clearly explained at the beginning of the survey. Participation was entirely voluntary, and respondents could withdraw without any consequences. All data collected were used exclusively for this study, ensuring the confidentiality and anonymity of the respondents.
RESULTS
The extent to which students at diverse educational levels utilize and perceive the role of ChatGPT as a tool for academic research
Table 1 presents the students’ perception of using ChatGPT in academic research. As can be observed in the table, the students perceived ChatGPT as very useful in various aspects of academic research (x ̅ = 3,42), such as in improving understanding of complex concepts related to research (x ̅ = 3,61), generating ideas and refining research questions (x ̅ = 3,57) and in enhancing the quality of academic writing (x ̅ = 3,47). Moreover, ChatGPT is perceived as moderately useful in identifying potential research gaps (x ̅ = 3,25) and finding relevant sources and references (x ̅ = 3,20).
|
Table 1. Distribution of Students’ Perceived Usefulness of ChatGPT in Academic Research |
|||
|
Statements |
x ̅ |
Std. Dev. |
Description |
|
ChatGPT helps me generate ideas and refine research questions. |
3,57 |
0,97 |
Very Useful |
|
ChatGPT assists me in finding relevant sources and references. |
3,20 |
1,13 |
Moderately Useful |
|
ChatGPT improves my understanding of complex concepts related to my research. |
3,61 |
1,05 |
Very Useful |
|
ChatGPT enhances the quality of my academic writing. |
3,47 |
1,07 |
Very Useful |
|
ChatGPT helps me identify potential research gaps in my field. |
3,25 |
1,05 |
Moderately Useful |
|
Note: N=316; 1,00-1,49= Not at all useful; 1,50-2,49= Slightly useful; 2,50-3,49= Moderately useful; 3,50-4,49= Very useful; 4,50-5,00= Extremely useful; Grand mean=3,42; Std. Dev.= 1,05 |
|||
Table 2 shows the students’ perception of the influence of ChatGPT on their academic performance. It can be noticed that the students perceived ChatGPT as moderately influential (x ̅ = 3,24) and positively influenced their academic performance (x ̅ = 3,32). Moreover, it has become moderately influential as well on their understanding of the subject matter (x ̅ = 3,32), in making research more efficient (x ̅ = 3,29) and in communicating research findings (x ̅ = 3,22), and in the achievement of higher grades in research (x ̅ = 3,04).
|
Table 2. Distribution of Student’s Perceived Influence of ChatGPT on Academic Performance |
|||
|
Statements |
x ̅ |
Std. Dev. |
Description |
|
ChatGPT has positively influenced my academic performance. |
3,32 |
1,02 |
Moderately Influential |
|
ChatGPT has helped me achieve higher grades in my research assignments or projects. |
3,04 |
1,05 |
Moderately Influential |
|
ChatGPT has improved my ability to effectively articulate and communicate my research findings. |
3,22 |
1,07 |
Moderately Influential |
|
ChatGPT has contributed to my overall understanding of the subject matter. |
3,32 |
1,05 |
Moderately Influential |
|
ChatGPT has made the research process more efficient for me. |
3,29 |
1,06 |
Moderately Influential |
|
Note: N=316; 1,00-1,49= Not at all influential; 1,50-2,49= Slightly influential; 2,50-3,49= Moderately influential; 3,50-4,49= Very influential; 4,50-5,00= Extremely influential; Grand mean=3,24; Std. Dev.= 1,05 |
|||
Table 3 illustrates the students’ perception of awareness of ethical considerations and concerns. It can be observed that the students are remarkably aware (x ̅ = 3,93), particularly of the possibility of plagiarism when using ChatGPT (x ̅ = 4,19) as well as relying too much on it and neglecting one’s critical thinking skills (x ̅ = 3,42). The students have also exhibited awareness of potential ethical concerns related to using ChatGPT (x ̅ = 3,96) and potential inaccuracies of information (x ̅ = 3,91). Furthermore, the students demonstrated awareness of the proper acknowledgment of the contribution of ChatGPT to their research work (x ̅ = 3,52).
|
Table 3. Distribution of Students’ Perceived Awareness of Ethical Considerations and Concerns |
|||
|
Statements |
x ̅ |
Std. Dev. |
Description |
|
I am aware of potential ethical concerns related to using ChatGPT for academic research. |
3,96 |
1,00 |
Aware |
|
I am concerned about the possibility of plagiarism when using ChatGPT. |
4,19 |
0,96 |
Aware |
|
I am cautious about relying too heavily on ChatGPT and neglecting my critical thinking skills. |
4,05 |
1,04 |
Aware |
|
I believe it is important to properly acknowledge the contribution of ChatGPT in my research work. |
3,52 |
1,06 |
Aware |
|
I am concerned about the potential bias or inaccuracies in the information provided by ChatGPT. |
3,91 |
1,01 |
Aware |
|
Note: N=316; 1,00-1,49= Not aware; 1,50-2,49= Slightly aware; 2,50-3,49= Moderately aware; 3,50-4,49= Aware; 4,50-5,00= Fully aware; Grand mean=3,93; Std. Dev.= 1,01 |
|||
Table 4 displays the students’ perception of ChatGPT’s likelihood for future use and recommendations. Students would somewhat likely use and recommend it (x ̅ = 3,26) specifically to schools to provide guidelines and policies on using ChatGPT (x ̅ = 3,61). In addition, the students will likely use more advanced versions of ChatGPT for academic research purposes (x ̅ = 3,46). Furthermore, the students will somewhat likely receive training or workshops on effectively integrating ChatGPT into my research process (x ̅ = 3,22) and recommend ChatGPT to other students for their academic research (x ̅ = 3,04). They rof continue using ChatGPT for academic research in the future (x ̅ = 2,97).
|
Table 4. Distribution of Student’s Perceived Likelihood for Future Use and Recommendations |
|||
|
Statements |
x ̅ |
Std. Dev. |
Description |
|
I intend to continue using ChatGPT for academic research in the future. |
2,97 |
0,97 |
Somewhat Likely |
|
I would recommend ChatGPT to other students for their academic research. |
3,04 |
1,03 |
Somewhat Likely |
|
I believe schools should provide guidelines or policies on using ChatGPT appropriately in academic research. |
3,61 |
1,16 |
Likely |
|
I think it would be beneficial to have rofes to more advanced versions of ChatGPT specifically designed for academic research. |
3,46 |
1,08 |
Likely |
|
I would like to receive training or workshops on how to effectively integrate ChatGPT into my research process. |
3,22 |
1,07 |
Somewhat Likely |
|
Note: N=316; 1,00-1,49= Very Unlikely; 1,50-2,49= Unlikely; 2,50-3,49= Somewhat likely; 3,50-4,49= Likely; 4,50-5,00= Very likely; Grand mean=3,26; Std. Dev.= 1,06 |
|||
The perceived benefits and challenges associated with the use of ChatGPT in academic research among students
This study further revealed how students perceive ChatGPT as a tool for aiding them with their academic research: providing additional information or resources; assisting with the mechanics, writing, paraphrasing, and improvement; generating ideas; simplifying or articulating ideas; reviewing literature; providing research gaps, research questions, and other sections in research; and analyzing data sets.
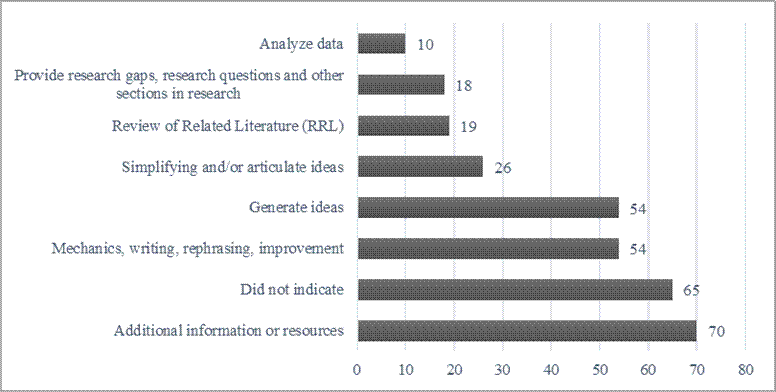
Figure 1. Students’ responses on the benefits of ChatGPT in Academic Research
In addition, this study also posited concerns students encounter while using ChatGPT for their research project: accessibility (e.g., requires a paid subscription to unlock unlimited features, internet connection to open the software); biased and inaccurate, making information unreliable; limited information and redundant; risk of plagiarism; sources or references are not provided, and links generated do not work (difficulty in searching for RRLs); time-consuming (e.g., prompts need to be phrased clearly so ChatGPT would understand); and overdependence on the software.
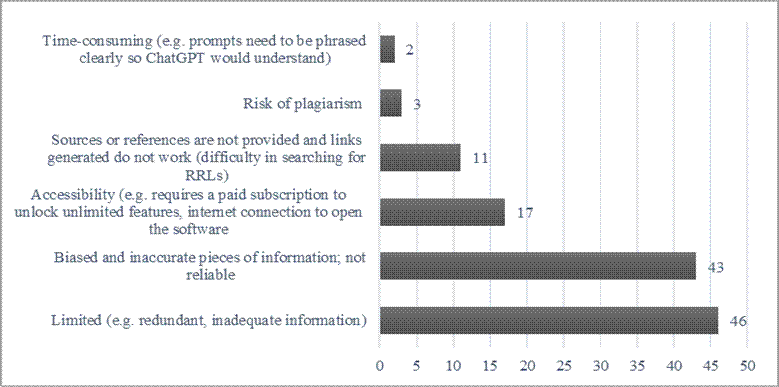
Figure 2. Challenges encountered while using ChatGPT
DISCUSSION
Artificial intelligence (AI) revolutionizes education with incredible tools and transformations like ChatGPT. ChatGPT is a conversational system designed to efficiently gather and refine information by converting it into text-based inputs tailored to the user’s specific needs. This study’s result indicates that ChatGPT can be a useful tool for Filipino students engaged in research if it is used responsibly. Zhai(74) supports this assertion by stating that ChatGPT can assist researchers in writing coherent, accurate, informative, and systematic papers. Additionally, ChatGPT can serve as a valuable tool in scientific and academic domains if used sensibly and ethically.
Furthermore, the results are consistent with the study conducted by Tanvir et al.(75), which states that ChatGPT has impacted students’ academic performance. However, Lo(13) mentioned that ChatGPT can be a potential virtual tutor for students. Still, there are challenges associated with its usage, such as generating incorrect information and bypassing plagiarism detectors, which consequently impairs students’ critical thinking.
According to Tlili et al.(76), the ethics of using ChatGPT in educational settings involve multifaceted considerations. However, creating thorough ethical rules for ChatGPT usage is the duty of the institution and the students to guarantee equitable and responsible use. In the study of Hasanein and Sobaih(28), 12 critical drivers of ChatGPT use for academic purposes in higher education were identified, namely quick response, ease of use, classroom and homework assistance, language proofreading and editing, problem-solving, data analysis, test preparation, research support, concept clarification, supplementary learning resource, adaptive learning and assessment activities. These identified drivers of ChatGPT are used to support the student’s likelihood of using it in their further academic endeavors.
Created by OpenAI in November 2022, ChatGPT has grown exponentially(8), becoming the most widely used and advanced chatbot thus far. Students can enhance the caliber and efficacy of their learning process by utilizing and maximizing AI-assisted technology. Moreover, this study’s findings are consistent with several studies on how ChatGPT is utilized as a resource. For instance, students say that ChatGPT promptly responds to their inquiries and offers supplementary materials that strengthen their understanding of an area of study.(37) Chatbots such as ChatGPT respond to user queries by generating ideal phrases, words, or images based on patterns and regularities found throughout the data.(77) It helps students draft with excellent proficiency and effectiveness(19,37) by guiding them with the technical aspects of research projects and academic papers, such as language translation and text generation. Additionally, it is a great tool that enhances the writing process.(78) In environments with artificial intelligence (AI) features, students receive immediate feedback utilizing an evaluation of their work and learning process.(1)
However, such a language model must be trained to analyze data, interpret results, and draw conclusions thoroughly. However, it can still be utilized to assist students as they go through the stages of the academic research process. Results indicate that the chatbot can help them suggest and formulate new research questions or hypotheses, allowing them to investigate different perspectives and enhancing their learning experience.(37) Using keywords or a specific research study subject, ChatGPT may also be a tool to sort through various research papers and find appropriate sources. ChatGPT performed some literature research and located the whole list of references for the text after a few more tries and inquiries.(79) Early on, throughout the research process, this can help researchers save time and effort. Further, ChatGPT can even assist researchers in finding new insights by helping them recognize emerging trends or patterns in textual data. It can answer questions requiring coding skills(6) and be able to render survival analysis and hazard ratios through generated codes by employing the programming language(41); however, it should also be noted that it is only partially a substitute for extensive statistical analysis.
With the numerous advantages of using AI technology in education, especially among students completing their research projects, it is also vital to be knowledgeable of their limitations. Similar to several other AI language chatbots, ChatGPT likewise requires internet connectivity for users to utilize fully; in fact, a paid subscription is highly recommended to optimize ChatGPT’s features such as plagiarism checker, citation generator, and privilege of unlimited searches, to name a few. However, more people use the internet simultaneously, causing a heavy server load or traffic volume. In that case, response time may still be delayed even when the connection is available.
Though seriously limited, ChatGPT is competent enough in some areas to provide an accurate and distinctive perception. However, users should also be careful because it can induce false perceptions(34) and fabricate information and references.(9,80) Because of its limitations, the current architecture of OpenAI’s GPT language model cannot generate references.(81) Because of this, when users ask it to provide sources or links, they typically fail to do so, and the absence of references renders it challenging to verify the accuracy of the data generated. Users are also concerned about ChatGPT’s inability to provide updated information due to its current design. It primarily uses data collected from 2021 and earlier and could not provide text-based outputs from 2022 onwards.(82)
Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots such as ChatGPT frequently need an extensive understanding of the textual inputs from the prompts they are trained to analyze. Thus, they heavily rely on the context of inputs, which can generate vague, inaccurate, or even too polished outputs, increasing their unreliability. Due to the surge in ChatGPT users, similar prompt input raises the risk of plagiarism. Several academics have also expressed concern about students exploiting AI technologies to plagiarize coursework or misusing AI to access research data.(11) Regardless of the number of times the user attempts to produce unique responses from the prompt, a variety but limited versions of statement structures generated from the outputs collected are only reconstructed and regenerated arbitrarily. Furthermore, with the increasing popularity of AI technologies like ChatGPT, users—including students—may become overly dependent on the features these chatbots offer, which could negatively impact the quality of their learning process and academic performance.
CONCLUSION
This study aims to determine the role of ChatGPT in academic research by examining the perspectives of Filipino students from diverse educational levels. It involves assessing how students use and perceive ChatGPT as a tool for academic research and identifying the benefits and challenges associated with its use. The results revealed ChatGPT to be moderately useful for various aspects of academic research and moderately influential in the student’s academic performance. Also, the students indicated that they knew the ethical considerations and concerns while using ChatGPT. Regarding the likelihood of ChatGPT’s future use and recommendations, the students indicated that they are likely to use the tool themselves and recommend it to other students.
Furthermore, this study found that students identified several benefits of using ChatGPT in academic research. The most common responses included receiving additional information or resources, getting help with mechanics, writing, paraphrasing, and generating ideas. On the other hand, students also faced challenges when using ChatGPT. They commonly encountered issues such as redundant, inadequate, and inaccurate information provided by ChatGPT and concerns regarding its accessibility and the potential for plagiarism.
Academic institutions should implement clear guidelines and regulations for responsible student use of ChatGPT to maximize benefits and mitigate potential issues. To ensure the accuracy of students’ academic work and address any biases in ChatGPT, this study also suggests adopting effective plagiarism detection systems for schools and informing students about them, particularly in academic research writing. Additionally, teachers should be provided with opportunities to enhance their understanding of AI tools in education, such as through participation in training sessions and conferences focused on integrating AI in education. ChatGPT is continuously upgraded to enhance its capabilities and become more user-friendly and practical. However, this study is limited to the students’ perceptions of using ChatGPT in academic research, including the benefits and challenges they encountered. While the findings of this study may not apply to all cases, they provide valuable insights into the potential experiences and considerations when using ChatGPT. Likewise, it is highly suggested that other researchers conduct related studies to understand this phenomenon better. Future studies could utilize a mixed methods approach and include other AI tools students utilize for academic research.
REFERENCES
1. Chen X, Xie H, Zou D, Hwang GJ. Application and theory gaps during the rise of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence [Internet]. 2020;1(1):100002. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666920X20300023
2. Tsai YC. Empowering learner-centered instruction: integrating ChatGPT python API and tinker learning for enhanced creativity and problem-solving skills. InInternational Conference on Innovative Technologies and Learning 2023 Aug 1 (pp. 531-541). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
3. Lund BD, Wang T, Mannuru NR, Nie B, Shimray S, Wang Z. ChatGPT and a new academic reality: Artificial Intelligence‐written research papers and the ethics of the large language models in scholarly publishing. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology. 2023 Mar 10;74(5).
4. Eke DO. ChatGPT and the rise of generative AI: Threat to academic integrity?. Journal of Responsible Technology. 2023 Apr 1;13:100060.
5. Lock S. What is AI chatbot phenomenon ChatGPT and could it replace humans. The Guardian. 2022 Dec 5;5. ---5
6. Scharth M. The ChatGPT chatbot is blowing people away with its writing skills. An expert explains why it’s so impressive. The Conversation. 2022 Dec 5.
7. Lee J, Soylu MY. ChatGPT and assessment in higher education. An interview with A. Goel and S. Harmon. Centre for 21st Century Universities. 2023 Mar.
8. Firat M. What ChatGPT means for universities: Perceptions of scholars and students. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching. 2023 Apr;6(1):57-63.
9. Rasul T, Nair S, Kalendra D, Robin M, de Oliveira Santini F, Ladeira WJ, Sun M, Day I, Rather RA, Heathcote L. The role of ChatGPT in higher education: Benefits, challenges, and future research directions. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching. 2023 May;6(1):41-56.
10. Wu X, Duan R, Ni J. Unveiling Security, Privacy, and Ethical Concerns of ChatGPT. Journal of Information and Intelligence [Internet]. 2023 Oct 1;2(2). Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2949715923000707
11. Sok S, Heng K. Opportunities, challenges, and strategies for using ChatGPT in higher education: A literature review. Sok, S., & Heng, K.(2024). Opportunities, challenges, and strategies for using ChatGPT in higher education: A literature review. Journal of Digital Educational Technology. 2023 Dec 15;4(1).
12. İpek ZH, Gözüm AI, Papadakis S, Kallogiannakis M. Educational Applications of the ChatGPT AI System: A Systematic Review Research. Educational Process: International Journal. 2023;12(3):26-55.
13. Lo CK. What Is the rofesion ChatGPT on Education? A Rapid Review of the Literature. Education Sciences [Internet]. 2023 Apr 1;13(4):410. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7102/13/4/410
14. Ma G. Chance or Challenge: The Role of ChatGPT in History Teaching and Historical Research in Higher Education. In2023 3rd International Conference on Education, Information Management and Service Science (EIMSS 2023) 2023 Sep 28 (pp. 869-874). Atlantis Press.
15. Rueda MM, Fernández-Cerero J, Fernández-Batanero JM, López-Meneses E. Impact of the implementation of ChatGPT in education: A systematic review. Computers. 2023 Jul 29;12(8):153.
16. Das SR, Madhusudan JV. Perceptions of Higher Education Students towards ChatGPT Usage. International Journal of Technology in Education. 2024;7(1):86-106.
17. Murad IA, Surameery NM, Shakor MY. Adopting ChatGPT to enhance educational experiences. International Journal of Information Technology & Computer Engineering. 2023;3(05):20-5.
18. Dergaa I, Chamari K, Zmijewski P, Saad HB. From human writing to artificial intelligence generated text: examining the prospects and potential threats of ChatGPT in academic writing. Biology of sport. 2023 Apr;40(2):615.
19. Wang M, Guo W. The potential impact of ChatGPT on education: Using history as a rearview mirror. ECNU Review of Education. 2023:20965311231189826.
20. Sánchez OV. Uso y percepción de ChatGPT en la educación superior. Revista de Investigación en Tecnologías de la Información. 2023 Jun 13;11(23):98-107.
21. Zayoud M, Oueida S, Pauly Aw, Ionescu S. Impact of Chatgpt on Education: Challenges and Opportunities. In International Conference of Management and Industrial Engineering 2023 Dec 19 (Vol. 11, pp. 75-82).
22. Graf A, Bernardi RE. ChatGPT in research: balancing ethics, transparency and advancement. Neuroscience. 2023 Apr 1;515:71-3.
23. Ngo TT. The perception by university students of the use of ChatGPT in education. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (Online). 2023;18(17):4.
24. Budjalemba AS, Listyani L. Factors Contributing to Students Difficulties in Academic Writing Class: Students Perceptions. UC Journal: ELT, Linguistics and Literature Journal. 2020 Dec 13;1(2):135–49.
25. Mahapatra S. Impact of ChatGPT on ESL students’ academic writing skills: a mixed methods intervention study. Smart Learning Environments. 2024 Feb 13;11(1):9.
26. Esplugas M. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance academic communication, education and research: a balanced approach. Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume). 2023 Sep;48(8):819-22.
27. Song C, Song Y. Enhancing academic writing skills and motivation: assessing the efficacy of ChatGPT in AI-assisted language learning for EFL students. Frontiers in Psychology. 2023 Dec 15;14:1260843.
28. Hasanein AM, Sobaih AE. Drivers and consequences of ChatGPT use in higher education: Key stakeholder perspectives. European journal of investigation in health, psychology and education. 2023 Nov 9;13(11):2599-614.
29. Dwivedi YK, Kshetri N, Hughes L, Slade EL, Jeyaraj A, Kar AK, Baabdullah AM, Koohang A, Raghavan V, Ahuja M, Albanna H. Opinion Paper:“So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management. 2023 Aug 1;71:102642.
30. Ding L, Li T, Jiang S, Gapud A. Students’ perceptions of using ChatGPT in a physics class as a virtual tutor. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education. 2023 Dec 22;20(1):63.
31. Romero Rodríguez JM, Ramírez-Montoya MS, Buenestado Fernández M, Lara Lara F. Use of ChatGPT at university as a tool for complex thinking: Students’ perceived usefulness.
32. Mercado HA, Morante LM. Experiences of Senior High School Mathematics Teachers in Out-of-field Teaching. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología-Serie de Conferencias. 2024 Aug 5;3:1125.
33. Strzelecki A. Students’ acceptance of ChatGPT in higher education: An extended unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. Innovative higher education. 2024 Apr;49(2):223-45.
34. Valova I, Mladenova T, Kanev G. Students’ Perception of ChatGPT Usage in Education. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science & Applications. 2024 Jan 1;15(1).
35. Baidoo-Anu D, Ansah LO. Education in the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): Understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Journal of AI. 2023 Dec;7(1):52-62.
36. Li A, Ye L. The Influence of ChatGPT on the Professional Development of Elementary Education Teachers and Its Countermeasures1. Frontiers in artificial intelligence and applications. 2023 Oct 26.
37. Limna P, Kraiwanit T, Jangjarat K, Klayklung P, Chocksathaporn P. The use of ChatGPT in the digital era: Perspectives on chatbot implementation. Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching. 2023 May 25;6(1).
38. Ming GK, Mansor M. Exploring the impact chat-GPT on teacher rofesional development: opportunities, challenges, and implications. Asian Journal of Research in Education and Social Sciences. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):54-67.
39. Mogavi RH, Deng C, Kim JJ, Zhou P, Kwon YD, Metwally AH, Tlili A, Bassanelli S, Bucchiarone A, Gujar S, Nacke LE. ChatGPT in education: A blessing or a curse? A qualitative study exploring early adopters’ utilization and perceptions. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans. 2024 Jan 1;2(1):100027.
40. Albayati, H. Investigating undergraduate students’ perceptions and awareness of using ChatGPT as a regular assistance tool: A user acceptance perspective study. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence. 2024 Jan 1;6:100203–3.
41. Shaengchart Y, Bhumpenpein N, Kongnakorn K, Khwannu P, Tiwtakul A, Detmee S. Factors influencing the acceptance of ChatGPT usage among higher education students in Bangkok, Thailand. Advance Knowledge for Executives. 2023 Oct;2(4):1-4.
42. Dempere J, Modugu K, Hesham A, Ramasamy LK. The rofesion ChatGPT on higher education. InFrontiers in Education 2023 Sep 8 (Vol. 8, p. 1206936). Frontiers Media SA.
43. Cotton DRE, Cotton PA, Shipway JR. Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innovations in Education and Teaching International [Internet]. 2023 Mar 13;61(2):228–39. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148
44. Rathod KD. A review of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Indian Scientific Journal of Research in Engineering and Management. 2023;7(07).
45. AlAfnan MA, Dishari S, Jovic M, Lomidze K. ChatGPT as an educational tool: Opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology. 2023 Mar 6;3(2):60–8.
46. Mogavi RH, Deng C, Kim JJ, Zhou P, Kwon YD, Metwally AH, Tlili A, Bassanelli S, Bucchiarone A, Gujar S, Nacke LE. ChatGPT in education: A blessing or a curse? A qualitative study exploring early adopters’ utilization and perceptions. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans. 2024 Jan 1;2(1):100027.
47. Zhang J, Abbas Z, Ali T, Liu Q, Wang Y. The Impact of ChatGPT on Students’ Writing Proficiency in Second Language Acquisition: Students’ Perception and Experiences: A Qualitative Analysis. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. 2024 Jan 5;4(1):1–9.
48. Crawford J, Cowling M, Allen KA. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice [Internet]. 2023 Mar 8;20(3). Available from: https://ro.uow.edu.au/jutlp/vol20/iss3/02/.
49. Steele JL. To GPT or not GPT? Empowering our students to learn with AI. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence. 2023 Jan 1;5:100160.
50. Hao, Y. The application and challenges of ChatGPT in educational transformation: New demands for teachers’ roles. Heliyon [Internet]. 2024 Jan 8;10(2):e24289. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844024003207
51. Su J, Yang W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Review of Education. 2023 Aug;6(3):355-66.
52. Pokkakillath S, Suleri J. ChatGPT and its impact on education. Research in Hospitality Management. 2023 Nov 1;13(1):31-4.
53. Sangarsu RR. Enhancing Student Engagement in Learning with Modern Web and AI Technologies. International journal of science and research. 2023 Oct 5;12(10):1439–42.
54. Yousuf M, Wahid A, Khan MY. Exploring the Effectiveness of AI Algorithms in Predicting and Enhancing Student Engagement in an E-Learning. International journal on recent and innovation trends in computing and communication. 2023 Nov 2;11(10):23–9.
55. Zhao S, Shen Y, Qi Z. Research on ChatGPT-Driven Advanced Mathematics Course. Academic Journal of Mathematical Sciences. 2023 Dec 20;4(5):42-7.
56. Villan F, Santos RP. ChatGPT as Co-advisor in scientific initiation: Action research with project-based learning in elementary education. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.14701. 2023 Nov 10.
57. Kim E, Ahn K. Exploring the potential of utilizing ChatGPT in professional English lesson planning and English language teaching. Co’deung yeong’eo gyo’yug. 2023 Dec 31;29(4):59–87.
58. Luo W, He H, Liu J, Berson IR, Berson MJ, Zhou Y, Li H. Aladdin’s Genie or Pandora’s Box for early childhood education? Experts chat on the roles, challenges, and developments of ChatGPT. Early Education and Development. 2024 Jan 2;35(1):96-113.
59. Thuy T, Can Van Da, Nguyen Van Hanh. The use of ChatGPT in teaching and learning: a systematic review through SWOT analysis approach. Frontiers in Education. 2024 Feb 9;9.
60. Yu Z. A Study of the Impact of ChatGPT on Secondary Education. The Educational Review, USA. 2023;7(7):939-42. –
61. Guan J, Zhang J, Zhang X. The Influence of Generative Artificial Intelligence on High School Students Academic Planning ChatGPT. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media. 2023 Nov 20;24(1):205–10.
62. Dao XQ, Le NB, Vo TD, Phan XD, Ngo BB, Nguyen VT, Nguyen TM, Nguyen HP. VNHSGE: VietNamese High School Graduation Examination Dataset for Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.12199. 2023 May 20.
63. Dao XQ, Le NB, Ngo BB, Phan XD. Llms’ capabilities at the high school level in chemistry: Cases of chatgpt and microoft bing ai chat.
64. Purnama I, Edi F, Wijanarko T. ChatGPT for teachers and students in science learning: A systematic literature review. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA. 2023 Oct 25;9(10):760-5.
65. Bau RT, Hermila A, Farman I, Hidayat LM, Salim S. AI Perspectives in Education: A BERT-based Exploration of Informatics Students’ Attitudes to ChatGPT. In2023 9th International Conference on Education and Technology (ICET) 2023 Oct 7 (pp. 36-41). IEEE.
66. Ayman SE, El-Seoud SA, Nagaty K, Karam OH. The Influence of ChatGPT on Student Learning and Academic Performance. In2023 International Conference on Computer and Applications (ICCA) 2023 Nov 28 (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
67. Santos OLD, Cury D. Challenging the Confirmation Bias: Using ChatGPT as a Virtual Peer for Peer Instruction in Computer Programming Education. In2023 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) 2023 Oct 18 (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
68. Dai W, Lin J, Jin H, Li T, Tsai YS, Gašević D, Chen G. Can large language models provide feedback to students? A case study on ChatGPT. In2023 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT) 2023 Jul 10 (pp. 323-325). IEEE.
69. Jeyaraman M, Ramasubramanian S, Balaji S, Jeyaraman N, Nallakumarasamy A, Sharma S. ChatGPT in action: Harnessing artificial intelligence potential and addressing ethical challenges in medicine, education, and scientific research. World Journal of Methodology. 2023 Sep 9;13(4):170.
70. Lund B, Ting W. Chatting about ChatGPT: How May AI and GPT Impact Academia and Libraries? SSRN Electronic Journal. 2023.
71. Farhi F, Jeljeli R, Aburezeq I, Dweikat FF, Al-shami SA, Slamene R. Analyzing the students’ views, concerns, and perceived ethics about chat GPT usage. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence. 2023 Nov 7:100180.
72. Spector PE. Do not cross me: Optimizing the use of cross-sectional designs. Journal of business and psychology. 2019 Apr 15;34(2):125-37.
73. Mutammimah H, Rejeki S, Kustini S, Amelia R. Understanding Teachers’ Perspective toward ChatGPT Acceptance in English Language Teaching. International Journal of Technology in Education. 2024;7(2):290-307.
74. Zhai X. ChatGPT user experience: Implications for education. Available at SSRN 4312418. 2022 Dec 27.
75. Tanvir K, Islam MS, Sezan SB, Sanad ZT, Rahman AJ. Impact of ChatGPT on academic performance among Bangladeshi undergraduate students. International Journal of Research In Science & Engineering. 2023;35:18-28.
76. Tlili A, Shehata B, Adarkwah MA, Bozkurt A, Hickey DT, Huang R, Agyemang B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart learning environments. 2023 Feb 22;10(1):15.
77. Adiguzel T, Kaya MH, Cansu FK. Revolutionizing Education with AI: Exploring the Transformative Potential of ChatGPT. Contemporary Educational Technology [Internet]. 2023 Jul 1;15(3):ep429. Available from: https://www.cedtech.net/article/revolutionizing-education-with-ai-exploring-the-transformative-potential-of-chatgpt-13152
78. Neumann M, Rauschenberger M, Schön EM. “We need to talk about ChatGPT”: The future of AI and higher education. In2023 IEEE/ACM 5th International Workshop on Software Engineering Education for the Next Generation (SEENG) 2023 May 16 (pp. 29-32). IEEE.
79. Macdonald C, Adeloye D, Sheikh A, Rudan I. Can ChatGPT draft a research article? An example of population-level vaccine effectiveness analysis. Journal of global health. 2023;13.
80. Bitzenbauer P. ChatGPT in physics education: A pilot study on easy-to-implement activities. Contemporary Educational Technology [Internet]. 2023 Jul 1;15(3):ep430. Available from: https://www.cedtech.net/article/chatgpt-in-physics-education-a-pilot-study-on-easy-to-implement-activities-13176
81. Hillier M. Why does ChatGPT generate fake references. TECHE. 2023 Feb.
82. Wen J, Wang W. The future of ChatGPT in academic research and publishing: A commentary for clinical and translational medicine. Clinical and Translational Medicine. 2023 Mar;13(3).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We sincerely thank the respondents for sharing their time and insights, the administration for their unwavering support and permission to conduct this study, and the reviewers for their assistance in improving this paper.
FINANCING
The study was not sponsored by any funding agency or research institution.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Jomar C. Cabuquin.
Data curation: Jomar C. Cabuquin, Romer F. Beltran Yu.
Formal analysis: Jomar C. Cabuquin, Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre, Mary Ann A. Manabat, Mary Grace H. Aruta.
Research: Jomar C. Cabuquin, Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre, Mary Ann A. Manabat, Mary Grace H. Aruta, Julinito Sangutan, Romer F. Beltran Yu.
Methodology: Jomar C. Cabuquin, Romer F. Beltran Yu.
Resources: Julinito Sangutan.
Supervision: Jomar C. Cabuquin.
Validation: Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre, Mary Grace H. Aruta, Mary Ann A. Manabat, Julinito Sangutan, Romer F. Beltran Yu.
Drafting – original draft: Jomar C. Cabuquin, Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre, Mary Ann A. Manabat, Mary Grace H. Aruta.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Mary Grace H. Aruta, Jomar C. Cabuquin, Maria Aleja Sandra Acidre, Mary Ann A. Manabat, Julinito Sangutan, Romer F. Beltran Yu.