Categoría: Finance, Business, Management, Economics and Accounting
ORIGINAL
Regulation of e-commerce in a globalising world: challenges and opportunities
La regulación del comercio electrónico en un mundo globalizado: retos y oportunidades
Vitalii Volynets1
![]() *, Georgii Zhelef2
*, Georgii Zhelef2
![]() *, Viktoriia
Adamyk3
*, Viktoriia
Adamyk3 ![]() *, Оleksander
Yurchenko4
*, Оleksander
Yurchenko4 ![]() *, Maiia
Kramchaninova5
*, Maiia
Kramchaninova5 ![]() *
*
1Kyiv University of Tourism, Economics and Law, Department of Restaurant Service in Hotels. Kyiv, Ukraine.
2Interregional Academy of Personnel Management. Kyiv, Ukraine.
3Lviv Polytechnic National University, Department of Management and International Business. Lviv, Ukraine.
4Borys Grinchenko Kyiv Metropolitan University, Department of International Economy. Kyiv, Ukraine.
5Volodymyr Dahl East Ukrainian National University, Department of Economics and Entrepreneurship. Kyiv, Ukraine.
Cite as: Volynets V, Zhelef G, Adamyk V, Yurchenko О, Kramchaninova M. Regulation of e-commerce in a globalising world: challenges and opportunities. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias. 2024; 3:1140. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf20241140
Submitted: 09-02-2024 Revised: 05-05-2024 Accepted: 14-07-2024 Published: 15-07-2024
Editor: Dr.
William Castillo-González ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the rapid pace of technological development and the growing influence of the Internet on commercial relations require constant upgrading of the legal framework to protect consumers, ensure a competitive environment for business and combat cybercrime. Therefore, to effectively use the opportunities offered by e-commerce, adequate regulation is required to ensure a balance between the interests of businesses, consumers and the state.
Objectives: the study aims to analyse the problems of e-commerce regulation in the context of globalisation, identify key challenges and opportunities, and determine mechanisms to improve their effectiveness.
Method: the paper examines the theoretical aspects of e-commerce and its role in the digital economy by analysing the literature. Additionally, generalisation and systematisation methods were applied to summarise information on the importance of e-commerce in business processes. The statistical data analysis assessed the development dynamics of the global and Ukrainian e-commerce markets. Furthermore, a comparative analysis was conducted to identify this sector’s global trends and develop corresponding development strategies.
Results: the study indicates that e-commerce plays a crucial role in the success of companies on a global scale. This distribution channel enables businesses to expand their global presence and enhance competitiveness. The study indicates that e-commerce plays a crucial role in the success of companies on a global scale.
Conclusions: e-commerce has become a crucial aspect of global retail, enabling consumers to shop digitally anywhere. The Ukrainian e-commerce market is rapidly evolving, adapting to technological advancements and changing consumer demands.
Keywords: Commerce; Regulation; Globalization; Competitiveness; Business; Innovation; Technology.
RESUMEN
Introducción: El rápido ritmo del desarrollo tecnológico y la creciente influencia de Internet en las relaciones comerciales requieren una actualización constante del marco legal para proteger a los consumidores, garantizar un entorno competitivo para las empresas y combatir el cibercrimen. Por lo tanto, para aprovechar eficazmente las oportunidades que ofrece el comercio electrónico, se requiere una regulación adecuada para garantizar un equilibrio entre los intereses de las empresas, los consumidores y el estado.
Objetivos: El estudio tiene como objetivo analizar los problemas de la regulación del comercio electrónico en el contexto de la globalización, identificar los desafíos y oportunidades clave y determinar los mecanismos para mejorar su efectividad.
Método: El artículo examina los aspectos teóricos del comercio electrónico y su papel en la economía digital mediante el análisis de la literatura. Además, se aplicaron métodos de generalización y sistematización para resumir la información sobre la importancia del comercio electrónico en los procesos comerciales. El análisis de datos estadísticos evaluó la dinámica de desarrollo de los mercados de comercio electrónico global y ucraniano. Además, se realizó un análisis comparativo para identificar las tendencias globales de este sector y desarrollar las estrategias de desarrollo correspondientes.
Resultados: El estudio indica que el comercio electrónico juega un papel crucial en el éxito de las empresas a escala global. Este canal de distribución permite a las empresas ampliar su presencia global y mejorar su competitividad. El estudio indica que el comercio electrónico desempeña un papel crucial en el éxito de las empresas a escala global.
Conclusiones: El comercio electrónico se ha convertido en un aspecto crucial del comercio minorista global, permitiendo a los consumidores comprar digitalmente en cualquier lugar. El mercado de comercio electrónico ucraniano está evolucionando rápidamente, adaptándose a los avances tecnológicos y a las cambiantes demandas de los consumidores.
Palabras clave: Сomercio; Regulación; Globalización; Competitividad; Negocios; Innovación; Tecnología.
INTRODUCTION
E-commerce has become a crucial sales channel for businesses of all sizes looking to expand their audience and gain a competitive edge in the modern world. The growth of the global economy and technological advancements have made this market segment particularly attractive. However, the increasing popularity of e-commerce has brought about new challenges, including the need to comply with various legislative norms in different countries, protect data, combat abuse and fraud, and ensure a high level of consumer trust.
The regulation of e-commerce requires constant updating and adaptation to new technological and economic challenges. Therefore, businesses and governments must be prepared for constant changes in the e-commerce sector to ensure its effective and stable functioning in the face of globalisation and technological innovations.
The purpose of this research article is to examine the issue of e-commerce regulation in the context of globalisation in order to identify critical challenges and opportunities. In addition, this topic requires systematising existing knowledge and deepening understanding of the problem, identifying trends and peculiarities of development, and offering practical recommendations for creating effective regulatory mechanisms.
The regulation of e-commerce presents a complex scientific problem characterized by evolving cybersecurity threats, dynamic business model transformations, and emerging global trends. This complexity underscores the need for comprehensive research into effective regulatory mechanisms and strategic adaptations in the e-commerce sector.
In this context, O.V. Bulak (1) investigated contemporary cybersecurity issues in the e-commerce sector and developed solutions to minimise the impact of cyber threats. Organisational measures were primarily used to achieve this goal. These measures included control and monitoring tools, standardisation, certification, external auditing, staff training, and developing a cybersecurity culture within companies and among e-commerce users. Companies in the e-commerce sector must comply with GDPR standards, particularly regarding cybersecurity requirements. The author identifies the importance of developing and implementing a reliable cybersecurity strategy. The strategy should be comprehensive, including regular risk assessments, staff training, cybersecurity incident response plans, and monitoring and threat control tools for e-commerce companies.
L.K. Glinenko and Yu.A. Daynovsky(2) conducted a scientific study which determined that extreme situations, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, impact the evolution of e-commerce business models. An analysis of changes in the components of these models confirmed that key innovations were implemented in areas such as consumer segments, their needs, value propositions, distribution channels, customer interaction methods, and revenue models. During their research, the authors identified ways to successfully transform e-commerce business models in Ukraine, ensuring sustainable development in crisis conditions.
O. Zayats and Ya. Kapko(3) investigated current trends in e-commerce development and found it to be a significant factor in global business expansion. The study identified China as a leading market in e-commerce, with the USA, China, and the UK being the preferred countries in terms of online market size. The study identified China as a leading market in e-commerce, with the USA, China, and the UK being the preferred countries in terms of online market size. The authors analysed the critical performance indicators and growth of e-commerce volumes in leading countries worldwide. They identified foreseeable trends in the development of this industry in the coming years. They particularly emphasised the significant trend of mobile commerce expansion.
In summary, addressing the scientific problem of e-commerce regulation involves a multifaceted approach that considers cybersecurity challenges, business model adaptability, and emerging global trends. Effective solutions must be developed to tackle these issues, ensuring robust regulatory frameworks, resilient business strategies, and proactive engagement with technological advancements.
METHODS
Context and Classification of the Study
The study focuses on the role of e-commerce as a crucial element of the digital economy, examining its impact on the internal and external operations of companies in the global and Ukrainian markets.
Universe and Sample
The universe of the study includes global and Ukrainian e-commerce markets. The sample consists of statistical data from various countries, focusing on e-commerce growth rates and market structure.
Study Variables
The dependent variable is the growth of the e-commerce market, measured by such indicators as sales volume, market penetration, and annual growth rate. The independent variables are technological advances, the regulatory environment, consumer preferences, and economic conditions.
Data Collection Methods and Instruments
A literature analysis was conducted to study the theoretical aspects of e-commerce, in particular, to understand its essence as an essential element of the digital economy; the method of generalisation was used to systematize and summarise information on the role of e-commerce in ensuring the efficient conduct of both internal and external operations of companies; an analysis of statistical data was applied to assess the dynamics of the global e-commerce market, as well as to study the structure of the Ukrainian e-commerce market; a comparative analysis was carried out to assess the growth rates of e-commerce in different countries to identify global trends in this sector and to determine development strategies for Ukrainian companies; the systematisation method was used to classify the main areas of recovery and development of the e-commerce market in Ukraine.
Statistical Techniques and Procedures
The research uses various statistical methods, such as trend analysis, comparative growth assessment and an estimation of the volume and structure of the e-commerce market.
Ethical Parameters
All data and sources used in this study are cited appropriately, ensuring the ethical use of information and maintaining the integrity of the research process. Data privacy and confidentiality are maintained throughout the study.
RESULTS
Electronic commerce (E-commerce) has revolutionised how economic relations are perceived between entities of different national economies. Instead of traditional methods of exchanging goods and services, a digital environment has emerged, where this exchange occurs quickly, efficiently, and globally thanks to computer technologies.(4) The success of electronic commerce depends on the use of global electronic networks for transmitting and exchanging data in business operations. It is imperative in international trade, where high-speed data transmission and global information technologies create new forms of cooperation between producers, intermediaries, and buyers, allowing business to be conducted without the limitations of geographical and cultural barriers. (5) The second factor is the unified global economic space, where consumers have developed more sophisticated demands for goods and services. Nowadays, consumers seek products that meet their specific needs, tailored to their requirements or a service provided in the most convenient format. Furthermore, customers anticipate accessing goods and services conveniently, challenging conventional working and service hours.(6)
Electronic commerce is a crucial element of the digital economy, covering all financial and trade transactions carried out through computer networks and associated business processes. It encompasses various aspects of the digital economy, including Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT), E-Trade, E-Cash, E-Marketing, E-Banking, E-Insurance, and more.(7) Electronic commerce is the sale of goods and services for profit, facilitated by technological tools. Its socio-economic essence is crucial, as information technologies serve to achieve this goal. The use of electronic platforms often leads to higher profitability than traditional commercial methods, making it particularly attractive for businesses.(8,9)
In addition, electronic commerce allows companies to adjust to the rapidly changing conditions of the global market and influence them actively, ensuring efficient internal and external operations. It includes convenient and flexible collaboration with global partners, enabling a quick response to customer requests and needs. Electronic commerce enables companies to select suppliers without being limited by location, thereby expanding their global market for products and services.(10) The main components of electronic commerce include mobile commerce, cashless payments, supply chain management, internet marketing, online transaction processing, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data analysis systems. Technological advancements in the semiconductor industry are driving the development of electronic commerce, creating new opportunities for innovative implementation and improved business practices.(11)
In recent years, electronic commerce has become an integral part of the global retail system, driving its transformation in the context of ongoing digitisation. It allows consumers worldwide to conduct profitable online transactions using various digital technologies. In 2020, over two billion people purchased goods or services online, resulting in a worldwide electronic retail sales volume of over 4,28 trillion US dollars (figure 1). It is essential to note the potential growth of the global e-commerce market, as retail sales have demonstrated impressive results projected until 2023. This dynamic highlights the importance of electronic commerce in the modern world, as it offers opportunities for global trade and economic growth.(12)
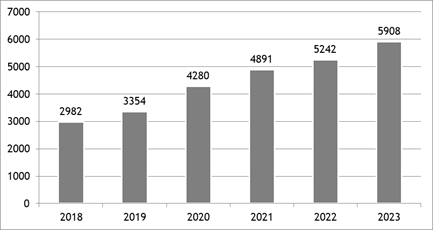
Source: Compiled by the author based on Berger and Galeta (13)
Figure 1. E-retail sales, billion USD
Electronic commerce is a crucial element of the global economy, providing significant potential for businesses and consumers. Forecasts predict a promising growth trajectory for this sector, with a substantial increase in retail sales expected by 2023. China, the USA, and France are identified as leaders in this process, demonstrating impressive rates of electronic commerce development (table 1). (14)
|
Table 1. Global E-commerce Growth Forecast |
|||
|
Country |
2018 / billion USD |
2023 / billion USD |
Five-year growth |
|
China |
636,1 |
1806,1 |
70,3 % |
|
United States of America |
504,6 |
735,4 |
45,7 % |
|
France |
49,4 |
71,9 |
45,6 % |
|
Australia |
18,6 |
26,9 |
44,6 % |
|
Canada |
39,9 |
55,4 |
38,8 % |
|
Germany |
70,3 |
95,3 |
35,6 % |
|
United Kingdom |
86,5 |
113,6 |
31,3 % |
|
Japan |
81,7 |
103,6 |
26,8 % |
|
East Korea |
63,7 |
80,2 |
25,9 % |
|
Source: Compiled by the author based on Keenan(12) |
|||
Like many other countries, Ukraine is experiencing rapid electronic commerce growth. This growth is defined not only by rapid technological changes but also by evolving consumer needs. The domestic e-commerce market is structured into five main sectors, each reflecting the specificity of consumer preferences and demands (figure 2).
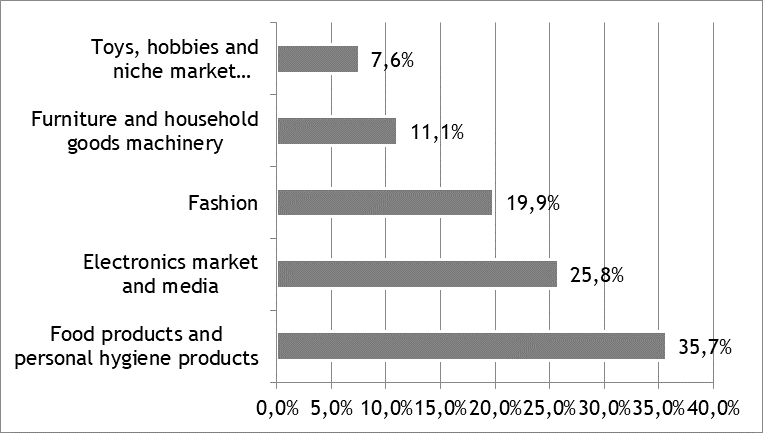
Source: Compiled by the author based on ECDB (15)
Figure 2. Structure of the Ukrainian E-commerce Market
To successfully address strategic tasks in electronic commerce, it is crucial to understand the dynamics of each sector. This understanding will enable Ukrainian companies to achieve high efficiency and competitiveness in the market.(16) The structure and dynamics of the e-commerce market are changing mainly due to the rapid progress of the digital economy and the growing popularity of online shopping.(17,18) In addition, due to changes in consumer preferences, specific categories of goods may become less popular. For instance, a decrease in demand may occur in the context of electronics and household appliances, which are typically large and expensive items whose cost depends on the foreign exchange rate. The market for building materials may experience growth as consumers increasingly focus on essential goods they have the greatest need for.(19,20) Research indicates that the online market is constantly growing. For example, Deloitte reports that since 2020, online sales have grown at twice the rate of offline sales, demonstrating the increasing popularity of online shopping among consumers. However, offline sales channels remain essential as many businesses continue to utilise physical stores and integrate them with the development of online sales.(18)
The development of e-commerce in Ukraine is leading to significant transformations in the domestic market, occurring against the backdrop of widescale changes in consumption, production, and trade methods (figure 3). The transition to the digital economy and the use of the Internet for buying and selling offer new opportunities for businesses and consumers. Although Ukraine’s e-commerce market ranks 48th globally, it still has growth potential (14). Consumers are gradually gaining trust in online purchases, and companies are actively adapting to the digital reality by developing new internet-oriented strategies and tools. In this context, Ukrainian national companies can interact in domestic and international markets, thanks to their access to global electronic platforms.(21,22)
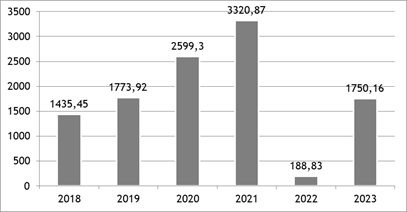
Source: Compiled by the author based on Kublitska (23)
Figure 3. Revenue of the E-commerce Market in Ukraine, mln. USD
The income dynamics in the e-commerce market are influenced by the full-scale invasion and global economic difficulties caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and war. Businesses have had to adapt to new realities due to sharp reductions in income and consumer behaviour changes to survive and recover. However, despite temporary difficulties, the e-commerce market continues to develop. Consumers and businesses adapt intensively to new conditions, anticipating further successful evolution.(24,25)
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly affected global trade and spurred the rapid development of e-commerce in Ukraine and worldwide. The pandemic crisis has led to the emergence of new companies, expansion of customer bases, diversification of goods, and new online payment methods in e-commerce. The development of e-commerce offers vast opportunities for a global audience of consumers, providing access to a wide range of goods and services. The popularity of mobile commerce, simplified purchasing processes, promotions, and secure online payments contribute to the increasing sales volumes in various segments of electronic commerce.(23)
Before the full-scale invasion, the domestic electronic market exhibited a trend towards increasing the proportion of the population utilising the Internet. Based on EcommerceEurope data for 2022, this proportion was approximately 67 %, representing a 5 % increase from the previous period. However, as of 2022, the population has decreased due to significant migration processes and the temporary occupation of parts of the country’s territory. Nevertheless, 85 % of citizens have access to the Internet. The report shows that approximately 44 % of Internet users make online purchases, indicating a trend towards the growth of the digital economy. Thus, despite a decrease of approximately 23 % in the total population, the percentage of Internet users has remained relatively stable. It suggests that e-commerce in Ukraine has the potential for growth and stability. (26, 27)
Furthermore, due to inflationary processes, there has been a simultaneous decrease in the proportion of the population residing in Ukraine and actively making online purchases with sufficient purchasing power. These trends are causing a slowdown in the development of the e-commerce market. The increasing popularity of e-commerce has resulted in more frequent purchases, intensifying competition among companies for consumer attention and loyalty. Automated marketing tools can be used to provide a personalised approach to consumer needs, which can increase their loyalty and activity. Therefore, the development of e-commerce will continue to require enterprises to refine their marketing strategies and compete effectively in this dynamic market.(27)
The COVID-19 pandemic and military events have significantly altered the consumer behaviour of Ukrainian shoppers. In 2021, approximately 60 % of respondents indicated that quarantine restrictions had little influence on their habits. However, by 2022, market turbulence proved to be much more severe. Firstly, the crisis reduced household incomes, resulting in decreased consumer demand and, consequently, retail sales volumes. Panic buying among consumers led to an increase in the average bill. By the end of 2022, the average online shopping bill amounted to USD 42,25 despite declining purchasing power. Although this amount is lower than in many European countries, it still significantly exceeded the previous year’s figures. The rapid growth in demand presents a significant challenge for e-commerce businesses. Inventory levels may be limited, and supplier access may be complicated due to disruptions in logistic chains, resulting in sharp price increases. (28)
Various regulatory strategies are employed in the e-commerce sector, with diverse business models actively utilised. Specifically, internet stores, classified ad platforms, marketplaces, and price aggregators can be highlighted. In recent years, marketplaces, internet stores, and social networks have become the primary channels for distributing goods and services. Promodo reports that the Ukrainian e-commerce market is dominated by several influential marketplaces, including Rozetka, Prom.ua, Epicentrk.ua, Bigl, Zakupka, and Allo, which account for 82,6 % of the market. The sector’s major stores, such as Comfy, Foxtrot, Citrus, Eldorado, and MOYO, account for 14,8 % of the market, while multi-category enterprises represent only 2,6 %.(29)
Despite the challenges and issues accompanying e-commerce development in Ukraine, the sector has demonstrated resilience and gradual progress. The recovery and development of the e-commerce market in Ukraine are influenced by various factors, including technological innovations and post-war recovery strategies (table 2).
However, despite significant expenses for the implementation of cutting-edge technological innovations, their profitability and high effectiveness in the long-term perspective play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and optimising the financial expenditures of the enterprise. These trends enable the creation of competitive advantages by utilising technological solutions currently unavailable to competitors.(30)
Thus, in global e-commerce practice, expected benefits are identified for companies and their customers. For companies, one of the main advantages is the opportunity for global presence, as national borders do not confine e-commerce but unfold within the worldwide Internet network. It allows even small businesses to conduct business transactions worldwide and significantly reduces advertising costs, enhancing their competitiveness. (33) Moreover, international e-commerce technologies enable companies to get closer to their customers, providing expanded pre-sale and after-sale support and quickly responding to their inquiries and feedback.(34)
|
Table 2. Trends in the Restoration and Development of the E-Commerce Market in Ukraine |
|
|
Direction |
Features |
|
New business models |
Strategies and approaches that differ from traditional e-commerce models and are aimed at attracting and retaining customers using innovative methods of selling goods and services |
|
Growth of subscription trading |
A trend in which customers can subscribe to regular receipt of goods or services for a fee, which contributes to increased loyalty and stability in company revenues |
|
Omnichannel e-commerce |
A strategy that involves the availability and integration of various sales and customer interaction channels, such as websites, mobile applications, and physical stores to ensure maximum accessibility and convenience for customers |
|
Mobile commerce |
The process of trading and shopping via mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, which is one of the fastest growing segments of e-commerce |
|
Marketplaces as a business model |
Online platforms where different sellers can list their goods or services for sale, and buyers can choose from a wide range of products |
|
Personalisation of marketing efforts |
A strategy to create and deliver individualised offers and services to each customer based on their unique needs, interests and behaviour |
|
Spread of technological innovations |
Implementing and using the latest technologies, such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and virtual and augmented reality technologies, to improve processes and ensure competitive advantage in the e-commerce market |
|
Source: Compiled by the author based on Muzychenko (31) and Omelchuk (32) |
|
DISCUSSION
O. V. Bulak’s(1) research focused on the importance of organisational measures in ensuring cybersecurity in the e-commerce sector. The author correctly identifies that measures such as control and monitoring, standardisation and certification, staff training, and developing a cybersecurity culture within companies are necessary for adequate protection against cyber threats. However, it is essential to consider the dynamic nature of cyber threats and continually update security measures in response to new threats and technological advancements. Furthermore, cooperation and information exchange among companies in e-commerce is crucial in collectively resisting threats.
This viewpoint is supported by L.K. Glinenko and Yu.A. Daynovsky,(2) who conducted research demonstrating how extreme situations, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, significantly impact the evolution of e-commerce business models. Their analysis of changes in the components of business models confirms the importance of innovation in crucial aspects such as consumer segments, consumer needs, and interaction methods, which in turn affect value propositions and distribution channels. The authors’ potential for successfully transforming e-commerce business models in Ukraine, ensuring sustainable development in crisis conditions, is agreed upon.
O. Zayats and Ya. Kapko’s(3) research identifying critical trends in the development of e-commerce in the modern world is also agreed upon. Additionally, China is acknowledged as a leader in the e-commerce market, followed by the USA and Europe. The authors noted that mobile commerce is a promising direction for developing e-commerce. Based on their research, they concluded the necessity of adapting to new conditions and creating global policy standards aimed at the sustainable growth of this sector.
CONCLUSION
Regulating electronic commerce in the context of globalisation is an important issue that requires attention and the development of effective strategies. The structure and nature of the e-commerce market are continuously changing due to the rapid development of the digital economy and the increasing popularity of online trading. The challenges posed by full-scale invasions and pandemics have stimulated the development of e-commerce, emphasising the need for adaptation and innovation. In current challenges, new opportunities emerge for businesses seeking to enhance efficiency and competitiveness. Modern business models, mobile commerce, personalised marketing, and technological innovations offer fresh perspectives and possibilities for businesses in a dynamic economic landscape. Enterprises can achieve success and stability in the global e-commerce market by adapting to new conditions, effectively regulating this sphere, and utilising existing opportunities.
REFERENCES
1. Bulak OV. Development of cyber security in electronic commerce under globalisation. Scientific Notes of Lviv University of Business and Law 2023; 37: 298-306. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3549020
2. Glinenko LK, Daynovsky YuA. The influence of certain global factors on the development of e-commerce business models. Marketing and digital technologies 2023; 7(4): 21-52. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/377096106_Impact_of_certain_global_factors_on_the_development_of_e-commerce_business_models
3. Zayats O, Kapko Ya. Current trends of development of electronic commerce. Economy and Society 2023; 55: 9.
4. Potwora M, Zakryzhevska I, Mostova A, Kyrkovskyi V, Saienko V. Marketing strategies in e-commerce: personalised content, recommendations, and increased customer trust. Financial and Credit Activity: Problems of Theory and Practice 2023; 5(52): 562-573.
5. Podra OP, Rogozhynska AV. Peculiarities of the development of electronic business in the conditions of the formation of the digital economy. Management and entrepreneurship in Ukraine: stages of formation and development problems 2023; 5(1): 224-235.
6. Bateyko VS. Development of electronic commerce in the conditions of globalisation. Master’s qualification work (051 “Economics”). NTU “KPI named after I. Sikorsky” 2021; 92. https://ela.kpi.ua/server/api/core/bitstreams/bba5c7ef-b593-4c42-aeae-1944aa9361c1/content
7. Chudna AD. Electronic commerce as a special format of business organisation. Entrepreneurship and trade: development trends. In materials of the 4th International Scientific Conference. Odesa Polytechnic State University 2021; 271-273. https://economics.net.ua/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/tezy.pdf#page=255
8. Perevozova IV, Orlova OI, Sakun AZh, Morozova OS, Pyasta AR. Development of innovative strategies for strengthening consumer loyalty in the field of e-commerce. Academic Visions 2024; 27: 11. https://academy-vision.org/index.p hp/av/article/view/895
9. Shevchenko I, Lysak O, Zalievska-Shyshak A, Mazur I, Korotun M, Nestor V. Digital economy in a global context: world experience. International Journal of Professional Business Review 2023; 8(4). http://dx.doi.org/10.26668/businessreview/2023.v8i4.1551
10. Bisikalo OV, Yurchuk MS. Classification of chat-bots for electronic commerce. Modern youth in the world of information technologies: materials of the 3rd Ukrainian scientific and Practical Internet Conference of young scientists and higher education students dedicated to Science Day. Vyshemirsky V.S. Book Publishing House 2022; 27-29. http://www.ksau.kherson.ua/konferenc/8049-conf-20220516.html
11. Zatonatska T, Volvach O. Current state of the Ukrainian market of electronic payment systems. World of Finance 2021; 2(67): 118-128.
12. Keenan M. Global Ecommerce Explained: Stats and Trends to Watch in 2021. Shopify 2023. https://www.shopify.com/enterprise/blog/global-ecommerce-statistics
13. Berger A, Galeta A. Global e-commerce development trends taking into account the crisis conditions of the COVID-19 pandemic. Economy and society 2021; 26: 7.
14. Yatsenko OM, Gryazina AS, Shevchyk OO. Electronic commerce as an element of the global trade system. Actual problems of economics 2019; 8(218): 4-15. https://ir.kneu.edu.ua/handle/2010/32689
15. ECDB. eCommerce market in Ukraine. EcommerceDB 2023. https://ecommercedb.com/markets/ua/all
16. Turzhanskyi A. Analysis of the current state and prospects for the development of Internet trade in Ukraine. Master’s qualification thesis (051 Economics). National Aviation University 2023; 87. https://er.nau.edu.ua/handle/NAU/62413
17. Dutchak S, Opolska N, Shchokin R, Durman O, Shevtsiv M. International aspects of legal regulation of information relations in the global internet network. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues 2020; 23(3): 1-7
18. Kuybida V, Savitska S, Shkoda M, Akhromkin I, Pron L, Kolomiiets Y. Methodology of development of social investment projects for the economy: legal aspects. Journal of Law and Sustainable Development 2023; 11(4): art. no. e0902. https://doi.org/10.55908/sdgs.v11i4.902
19. Matskiv H, Raiter N. Trends of development of electronic commerce. Bulletin of Lviv National Environmental University. Series “AIC Economics” 2023; 30: 163-169.
20. Simonenko K. The impact of war on online commerce: how online sales of retailers changed during the first half of 2022. The Retail Association of Ukraine 2022. https://rau.ua/novyni/vpliv-vijni-na-internet/
21. Skrigun NP, Rozumei SB, Molin NO. Online and offline tools in the system of integrated marketing communications. Marketing and digital technologies 2022; 6(2): 49-61. https://mdt-opu.com.ua/files/download/2022/mdt_6.2.2022.pdf
22. Meshcheriakov A, Bodenchuk L, Liganenko I, Rybak O, Lobunets T. Trends in the Development of the Banking System of Ukraine under Conditions of Military Actions and Globalization Influences. Financial and Credit Activity: Problems of Theory and Practice 2023; 3(50): 8-22. https://doi.org/10.55643/fcaptp.3.50.2023.3993
23. Kublitska O. The e-commerce market in Ukraine: current state and post-war recovery trends. Problems and prospects of economics and management 2023; 3(35): 98-108. http://dx.doi.org/10.25140/2411-5215-2023-3(35)-98-108
24. Suárez YS, Laguardia NS. Trends in research on the implementation of artificial intelligence in supply chain management. LatIA 2023;1:6–6. https://doi.org/10.62486/latia20236.
25. Kozhyna A, Razina T, Kravchenko A, Kuprii T Melnyk T. Human capital development in the context of globalization processes: Regulatory aspect. Economic Affairs (New Delhi) 2022; 67(4): 887-895. http://ndpublisher.in/admin/issues/EAv67n4sv.pdf
26. Osiik D. Online trade in Ukraine in 2022: Ukrainian Internet trends and the impact of the war. The Retail Association of Ukraine 2022. https://rau.ua/novyni/digital-v-ukraini-2022-trends/
27. Bondarenko SO, Makeieva O, Usachenko V, Veklych T, Arifkhodzhaieva, Lernyk S. The legal mechanisms for information security in the context of digitalization. Journal of Information Technology Management 2022; 14: 25-58. https://jitm.ut.ac.ir/article_88868.html
28. Lyakhovchenko VE. Integration of the online store into the information system supporting the activities of enterprises. Master’s qualification thesis (029 Information, library and archival work). Donetsk National University named after V. Stus 2024; 74. https://jqmth.donnu.edu.ua/article/view/14957/14863
29. Global24.com. Online sales: Ukraine ecommerce 2023 Analysis. Global24.com 2023. https://global24.com/en/blog/online-sales-ukraine-ecommerce-2023-analysis/#pll_switcher
30. Shkil L. 10 figures about Ukrainian e-commerce – research by Promodo. AIN 2021. https://ain.ua/2021/12/13/10-czyfr-yaki-zminyly-ukrayinskyj-ecommerce/
31. Muzychenko TO, Skorba OA, Shevchuk AA. Artificial intelligence as a means of optimising business processes in e-commerce. Academic Visions 2023; 25: 13.
32. Omelchuk S. Omni-channel in internet commerce. Innovative technologies of marketing and management in conditions of transformational changes: theses of the International Scientific and Practical Conference. KhNU 2023; 8: 133-136
33. Dybchuk LV. Trends and forecast of development e-commerce in Ukraine and in the world. Regional Economy and Management 2019; 1(23): 52-56.
34. Smoliy L, Kostyuk V. Latest trends and perspectives of the development of electronic commerce in international business. Economy and society 2021; 29: 7. https://doi.org/10.32782/2524-0072/2021-29-43
FINANCING
The authors did not receive funding for the development of this research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Data curation: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk.
Formal analysis: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Research: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Methodology: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Project management: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef.
Software: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Supervision: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Validation: Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Display: I Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Drafting – original draft: Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.
Writing – proofreading and editing: Vitalii Volynets, Georgii Zhelef, Viktoriia Adamyk, Оleksander Yurchenko, Maiia Kramchaninova.