ORIGINAL
Research methods in cultural studies
Métodos de investigación en estudios culturales
Liudmyla Polishchuk1 ![]() *, Olena Hubernator1
*, Olena Hubernator1 ![]() *, Volodymyr Pylypiv1
*, Volodymyr Pylypiv1 ![]() *, Iryna Shvets1
*, Iryna Shvets1 ![]() *, Oleksandr Kabanets1
*, Oleksandr Kabanets1 ![]() *
*
1Kyiv National University of Culture and Arts, Department of Event Management and Leisure Industry, Kyiv, Ukraine.
Cite as: Polishchuk L, Hubernator O, Volodymyr Pylypiv VP, Shvets I, Kabanets O. Research methods in cultural studies. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias. 2024; 3:.712. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2024.712
Submitted: 27-02-2024 Revised: 24-06-2024 Accepted: 02-10-2024 Published: 03-10-2024
Editor: Dr.
William Castillo-González ![]()
Corresponding author: Liudmyla Polishchuk *
ABSTRACT
Introduction: the issue of using research methods in cultural studies is a key factor in the analysis of cultural phenomena and processes. Contemporary approaches include hermeneutics, structuralism, semiotics, ethnographic, comparative, phenomenological, sociological, and psychoanalytic methods. Each of them provides unique tools for cultural research.
Objective: the purpose of the study is to analyze the effectiveness of various research methods in cultural studies and to identify their advantages and disadvantages in the conditions of modern challenges. The research methodology involves the analysis of the structural components of cultural studies and the possibility of applying variable methods for their identification.
Method: the research sample consists of a set of methods: hermeneutics, structuralism, semiotics, ethnographic, comparative, phenomenological, sociological and psychoanalytical. The article examines the practices of applying methods for the interpretation of cultural texts, the analysis of structural elements of cultural systems.
Results: results of the study emphasize the importance of the integration of interdisciplinary approaches and modern technologies to increase the effectiveness of cultural studies. The conclusions of the study indicates the need to adapt traditional methodological approaches to the conditions of globalization and cultural hybridization. Prospects for further research are aimed at the development of new methodological tools and the use of modern technologies for data collection and analysis. Special attention should be paid to international cooperation and exchange of experience between researchers for the development of global cultural knowledge.
Conclusions: research methods in cultural studies are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of cultural phenomena, but they face challenges such as subjectivity in interpretation, necessitating improved methodologies and interdisciplinary cooperation.
Keywords: Cultural Methods; Set of Approaches; Principles; Cognitive Process; Practical Activity; Scientific and Practical Aspect.
RESUMEN
Introducción: la cuestión del uso de métodos de investigación en los estudios culturales es un factor clave en el análisis de los fenómenos y procesos culturales. Los enfoques contemporáneos incluyen la hermenéutica, el estructuralismo, la semiótica, los métodos etnográficos, comparativos, fenomenológicos, sociológicos y psicoanalíticos. Cada uno de ellos proporciona herramientas únicas para la investigación cultural.
Objetivo: el propósito del estudio es analizar la efectividad de varios métodos de investigación en los estudios culturales e identificar sus ventajas y desventajas en las condiciones de los desafíos modernos. La metodología de investigación implica el análisis de los componentes estructurales de los estudios culturales y la posibilidad de aplicar métodos variables para su identificación.
Método: la muestra de investigación consta de un conjunto de métodos: hermenéutico, estructuralista, semiótico, etnográfico, comparativo, fenomenológico, sociológico y psicoanalítico. El artículo examina las prácticas de aplicación de métodos para la interpretación de textos culturales, el análisis de elementos estructurales de los sistemas culturales.
Resultados: los resultados del estudio enfatizan la importancia de la integración de enfoques interdisciplinarios y tecnologías modernas para aumentar la efectividad de los estudios culturales. Las conclusiones del estudio indican la necesidad de adaptar los enfoques metodológicos tradicionales a las condiciones de la globalización y la hibridación cultural. Las perspectivas de investigación futuras apuntan al desarrollo de nuevas herramientas metodológicas y al uso de tecnologías modernas para la recopilación y el análisis de datos. Se debe prestar especial atención a la cooperación internacional y al intercambio de experiencias entre investigadores para el desarrollo del conocimiento cultural global.
Conclusiones: los métodos de investigación en los estudios culturales son cruciales para una comprensión integral de los fenómenos culturales, pero se enfrentan a desafíos como la subjetividad en la interpretación, lo que requiere metodologías mejoradas y cooperación interdisciplinaria.
Palabras clave: Métodos Culturales; Conjunto de Enfoques; Principios; Proceso Cognitivo; Actividad Práctica; Aspecto Científico y Práctico.
INTRODUCTION
Cultural studies as a science is of fundamental importance for the understanding and interpretation of various cultural phenomena and processes occurring in societies. It explores the essence of culture, its structure, functions and development in different historical periods and geographical contexts. The author (1) believes that cultural studies covers a wide range of issues, including the study of material and spiritual culture, religious beliefs, art, literature, language and traditions. The development of cultural studies took place through the integration of knowledge from various fields, such as anthropology, sociology, history, philosophy and linguistics. It was they who contributed to the formation of a comprehensive approach to the study of culture. Culturology was able to become an interdisciplinary science capable of deeply analyzing and understanding complex cultural and ethical phenomena.
The use of current research methods in cultural studies is extremely important to achieve accurate results. The methodological apparatus of cultural studies includes various approaches and techniques, such as hermeneutics, structuralism, semiotics, and others. According to E. S. Eshak(2) each of the methods has its own characteristics that allow researchers to focus on different aspects of cultural phenomena. Hermeneutics focuses on the interpretation of texts and symbols, while structuralism analyzes cultural phenomena through their structures and relationships. Semiotics studies sign systems and symbolism, while ethnography allows for field research and direct observation of cultural practices. The importance of current methods is that they provide a multidimensional approach to the study of culture.
Due to the development of globalization and integration of cultures, research is gaining special importance. The article (3) states that globalization has caused an intensive exchange of cultural values, ideas, traditions and practices between different peoples, which has led to the emergence of new cultural forms. They have created new challenges for researchers who must take into account the dynamics of cultural change and the interaction of different cultural elements. The integration of cultures increases the need for research aimed at understanding the processes of cultural hybridization, transformation and preservation of cultural heritage. It is important to study how globalization affects cultural identity and social structures, how different cultures adapt to new conditions. In general, cultural studies are becoming a key science for analyzing and understanding the modern world, where cultural interactions and changes occur with unprecedented speed and intensity.
Literature review
Scientists pay attention to the analysis of the application of cultural studies methods, which are a tool for understanding cultural phenomena and processes. Research (4) emphasizes the importance of hermeneutics as a method that allows for the analysis and interpretation of cultural texts, which contributes to a better understanding of cultural meanings and symbols. The importance of the structuralist approach is highlighted in the work (5), where cultural phenomena are analyzed through their structural elements, which allows to reveal the internal regularities of cultural systems. According to research (6) semiotics, as the science of sign systems, is a key method for studying the symbolic aspects of culture, which helps reveal hidden meanings in cultural artifacts.
The use of the ethnographic method is analyzed in a study (7), where the authors describe field research as an effective way of gathering data about cultural practices and customs. Research (8) draws attention to the importance of the comparative method, which allows studying the cultural phenomena of different peoples, which helps to identify both common and unique features. The author (9) analyzes the phenomenological method focused on the study of subjective experience and perception of cultural phenomena. This method allows you to understand how people interpret and interact with cultural forms. The article (10) considers the sociological method as a tool for analyzing cultural phenomena through the prism of social structures and relationships, which allows understanding the influence of social factors on culture.
Despite the effectiveness of these methods, there are significant problems and challenges that complicate cultural studies. Research points to the problem of subjectivity of interpretations, which can lead to different interpretations of the results.(11) Globalization, as noted in the work (12), causes rapid changes in cultures, which calls into question traditional methodological approaches and requires adaptation to new conditions. The article (13) analyzes the problem of cultural hybridization, which complicates the classification and analysis of new cultural forms arising from the interaction of different cultures.
The study (14) emphasizes the importance of the integration of various scientific disciplines, such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, which allows obtaining objective and comprehensive results. The author (15) emphasizes the importance of international cooperation and exchange of experience between researchers from different countries, which contributes to the development of global cultural knowledge. The implementation of these measures is necessary to ensure a high level of research and development of cultural studies as a science.
The author (16) believes that the use of hermeneutics in cultural studies makes it possible to understand cultural texts and symbols. The scientist (17) notes that the structuralist approach to the study of culture is focused on the analysis of relationships between various elements of cultural systems. According to (18), the semiotic method is key to understanding sign systems and symbols in culture, allowing researchers to discover hidden meanings in media, literature, and other forms of cultural expression. The author (19) emphasizes the importance of the ethnographic method, which makes it possible to directly document cultural practices and customs.
The scientist (20) emphasizes the effectiveness of the comparative method, which allows studying the cultural phenomena of different peoples and identifying both common and distinctive features of their cultural practices. The study (11) highlights a phenomenological approach to the analysis of subjective experience and perception of cultural phenomena.
To overcome the uncertainty of analysis in cultural studies, the researcher (15) recommends improving methodological approaches by integrating interdisciplinary research. Further research should be focused on international cooperation and exchange of experience between researchers from different countries. This issue is a key factor for the development of global cultural knowledge and effective response to modern challenges in the field of culture.
Research goals
The purpose of the article is to analyze the effectiveness of modern research methods in cultural studies, with an emphasis on the integration of various approaches and technologies that meet the requirements of the modern globalized and multicultural world. The problem of the research focuses on identifying and analyzing the main challenges and barriers that researchers face when applying various methods in cultural studies. An important direction is the study of the potential of interactive and adaptive technologies for increasing the accuracy and depth of cultural studies. The tasks of the research are the determination of effective research methods, the analysis of existing methodological approaches, and the development of recommendations for improving research programs. The practical significance of the research is revealed in the possibility of applying its results to optimize research processes in scientific institutions, contributing to the formation of highly qualified specialists in the field of cultural studies. A promising direction is the study of the ability to effectively communicate in a multilingual, culturally diverse environment.
METHOD
The methodology of the article is aimed at a comprehensive analysis of structural components in cultural studies and the study of methods used to study cultural phenomena. Research consists of several key stages, each of which involves the use of specific methods and approaches to achieve a deep understanding of the subject. The research sample consists of a set of methods: hermeneutics, structuralism, semiotics, ethnographic, comparative, phenomenological, sociological and psychoanalytical.
The first stage of research includes the analysis of the theoretical foundations of cultural studies and the definition of the main structural components that form this scientific discipline. At this stage, methods of content analysis and literature review are used. Content analysis makes it possible to systematize scientific works on cultural studies, to identify the main topics, concepts and approaches used in this field. The literature review helps to generalize existing knowledge, identify gaps in research, and formulate the main directions for further analysis.
The second stage involves a detailed analysis of specific research methods used in cultural studies. This includes methods that are outlined in the study sample. Each method is considered separately from the point of view of its historical development, basic principles and applied significance. The analysis of methods is carried out through a critical review of scientific works, which allows to assessing their strengths and weaknesses, to identify the main directions of their application in modern research.
The third stage includes a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of various research methods in cultural studies. For this, a comparative method is used, which allows to identify the advantages and disadvantages of each of the considered methods, to assess their compliance with modern challenges and requirements of research practice. Special attention is paid to the analysis of the integration of methods and interdisciplinary approaches, which contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of cultural phenomena.
The final stage of the research involves the development of recommendations for improving methodological approaches in cultural studies. On the basis of the conducted analysis, proposals are formulated regarding the adaptation of existing methods to modern conditions, as well as the possibility of integrating new technologies and approaches. The stage includes discussion of prospects for international cooperation and exchange of experience between researchers, which will contribute to the development of global cultural knowledge. Thus, the research methodology involves an approach to the analysis of structural components and research methods in cultural studies as a global phenomenon.
RESULTS
Culturology is an interdisciplinary science that studies culture as a complex of social, material, spiritual, intellectual and aesthetic phenomena. The branch of knowledge investigates the processes of formation, transmission and transformation of cultural values, norms and practices in different societies. Cultural studies covers a wide range of topics, including language, art, religion, customs, rituals, and other aspects of human activity that influence the formation of cultural identity.(12) The development of cultural studies as a scientific discipline began in the middle of the 20th century and continues to develop thanks to the integration of knowledge from other scientific fields, such as anthropology, sociology, philosophy, history and literature.
Globalization has significantly affected culture, causing intensive processes of cultural exchange and integration between different peoples and countries. It promotes the spread of cultural products, ideas, values and practices at the global level, which leads to the emergence of new cultural forms and phenomena. The relevant process affects both the macro level, involving entire countries and regions, and the micro level, affecting individual cultural identities. Globalization creates the conditions for the growth of cultural hybridization, when elements of different cultures interact and create new, syncretic forms of culture. This phenomenon can be observed in all spheres of cultural activity, from music and cinema to fashion and cuisine. On the one hand, globalization promotes cultural enrichment and mutual understanding between peoples, but on the other hand, it leads to cultural. Its main structural components are shown in figure 1.
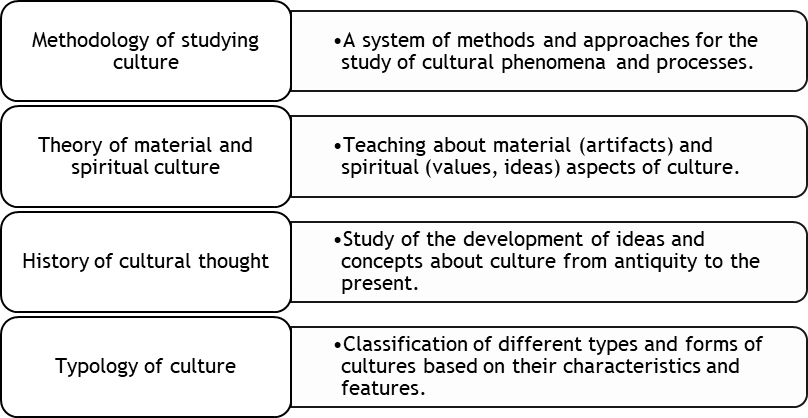
Figure 1. Structural components of cultural studies
Cultural studies use a wide range of methods and approaches to study cultural phenomena. One of the most common approaches is hermeneutics, which deals with the interpretation of cultural texts and symbols, which allows revealing deep meanings and meanings. Structuralism, proposed by Claude Lévi-Strauss, analyzes cultural phenomena through their structural elements and relationships, which allows revealing the subconscious structures that shape culture. Semiotics, developed by Roland Barthes, studies the sign systems and symbols used in culture and help to understand how meanings are constructed and transmitted through cultural signs. Ethnography involves field research where researchers directly observe and document cultural practices and customs, allowing for empirical data about a culture from the inside. The comparative method allows you to study the cultural phenomena of different peoples and identify both common and distinctive features, which contributes to a deeper understanding of cultural processes and patterns.
Psychological research methods in cultural studies make it possible to analyze how cultural factors affect psychological processes and vice versa. The psychoanalytic approach proposed by Sigmund Freud and developed by Carl Jung helps to understand the symbolic aspects of culture and the subconscious motives of human behavior. Analysis of cultural artifacts through the prism of psychoanalytic theories allows us to reveal deep, often unconscious meanings embedded in art, literature, and religious texts. Cognitive psychology helps to investigate how cultural factors affect the processes of perception, memory and thinking, which is important for understanding cultural differences in people’s worldview and behavior. The main methods used for research in cultural studies are listed in table 1.
|
Table 1. Research methods in cultural studies |
||
|
Research method |
Characteristic |
Application |
|
Hermeneutics |
Analysis and interpretation of texts to understand their content and meaning. |
Interpretation of literary works or religious texts. |
|
Structuralism |
Analysis of cultural phenomena through their structures and relationships. |
Study of myths and rituals of different cultures. |
|
Semiotics |
Study of sign systems and symbols in culture. |
Analysis of media and advertising. |
|
Cultural and historical |
Study of cultural phenomena in the context of their historical development. |
Study of the development of religious rites in different historical periods. |
|
Ethnographic |
Collection and analysis of data on cultural practices and customs through field research. |
Study of traditional rites in remote communities. |
|
Comparative |
Comparison of cultural phenomena of different cultures to identify common and distinctive features. |
Comparison of wedding ceremonies in different countries. |
|
Phenomenological |
Study of cultural phenomena through subjective experience and perception. |
Analysis of personal perception of religious experiences. |
|
Sociological |
Study of cultural phenomena through social structures and relationships. |
Study of the impact of social media on modern culture. |
|
Psychoanalytic |
Analysis of cultural phenomena through the lens of psychoanalytic theories such as the subconscious and symbolic meanings. |
Interpretation of symbols in art from the point of view of psychoanalysis. |
In pedagogical practice, the use of research methods in cultural studies contributes to the formation of students’ critical thinking, analytical skills and a deep understanding of cultural phenomena. The introduction of the hermeneutic method into the educational process allows students to learn to interpret cultural texts and symbols, which is important for the development of the ability to analyze and understand cultural contexts.
The future of interdisciplinary methods in cultural studies looks promising thanks to the constant development of technologies and new scientific approaches. The integration of digital technologies opens up new opportunities for the analysis of cultural phenomena. The use of automated systems allows researchers to analyze huge volumes of information, identify trends and patterns. Digital libraries contribute to the automation of analysis processes, which significantly increases the efficiency of research. A new phenomenon is the development of digital anthropology, which studies cultural practices in a virtual environment, opens new perspectives for the study of modern forms of communication and self-expression. An interdisciplinary approach combined with the latest technologies will allow cultural studies to adapt to rapid changes in the global cultural space, contributing to a deeper understanding of cultural processes and their impact on society.
DISCUSSION
Among researchers, the effectiveness of various research methods for use in cultural studies is actively discussed. The author (5) emphasizes the importance of hermeneutics for the interpretation of cultural texts, which is consistent with the conclusions about the need to understand cultural symbols. The results of the study reinforce the idea (9) about the importance of the structuralist approach, which allows revealing the internal regularities of cultural systems. On the other hand, own findings confirm the importance of semiotics (8) for the analysis of symbolic aspects of culture, which helps to reveal hidden meanings in cultural artifacts. An analysis (12) of the ethnographic method points to its effectiveness in investigating cultural practices through field research. The use of research methods in cultural studies is crucial for achieving accurate scientific results. The hermeneutic method allows the interpretation of cultural texts and symbols, revealing their meanings, which is extremely important for understanding cultural heritage and modern cultural processes.
The results of the article confirm the opinion (19) about the usefulness of the comparative method for identifying common and unique features of cultural phenomena. The obtained results confirm that the phenomenological method, as indicated in the article (5), is effective for understanding the subjective experience of people in the context of culture. The sociological method, as noted by (2), is key to analyzing the impact of social structures on culture, which is confirmed by the results obtained. A study (4) emphasizes the importance of a psychoanalytic approach to uncovering subliminal motives in cultural texts, which resonates with the paper’s hypothesis. Structuralism helps researchers analyze cultural phenomena through their structural elements and relationships. Semiotics studies sign systems and symbols used in culture, helping to understand how meanings are constructed and transmitted through cultural signs. The ethnographic method involves field research where researchers directly observe and document cultural practices and customs, which allows for empirical data. The use of existing methods provides a multidimensional approach to the study of culture, which is of primary importance for the accurate analysis of cultural processes.
Globalization and rapid cultural changes, as noted by (13), question traditional methodological approaches, confirming the need to adapt to new conditions. Ethnographic research in the educational process contributes to the development of field research skills, observation and documentation of cultural practices. The comparative method allows students to develop the skills of analysis and comparison of different cultural phenomena. The use of these methods in pedagogical practice helps students master the tools necessary for conducting cultural studies and develop the ability for independent critical thinking. The analysis (16) of cultural hybridization coincides with the experience of complications in the classification of new cultural forms. Conclusions (15) about the need for new methodological solutions for the study of modern cultural processes are confirmed by the results. Therefore, the comparison with other studies emphasized the importance of different research methods in cultural studies, revealed the need to adapt methodological approaches to the modern challenges of globalization and cultural hybridization.
CONCLUSION
Thus, research methods in cultural studies are extremely important for understanding various cultural phenomena and processes. They include various approaches. Each of these methods has its own specific tools and techniques that allow researchers to obtain a multidimensional picture of cultural processes and phenomena. The use of methods allows to interpret cultural texts and symbols, to study them in the context of social structures, historical periods and psychological factors. This contributes to a comprehensive and deep understanding of culture, which is necessary for the formation of a holistic view of human society and its development.
The application of research methods in cultural studies faces a number of global challenges due to the rapid development of related sciences. One of the main problems is the subjectivity of data interpretation, since a significant number of methods, such as hermeneutics and phenomenology, depend on the personal beliefs and experiences of the researcher. To overcome existing problems, it is necessary to improve methodological approaches and develop new research tools. It is important to ensure an interdisciplinary approach to the study of culture, involving representatives of various sciences in cooperation. In further research, it is important to stimulate international cooperation and exchange of experience between researchers from different countries. It is this approach that will contribute to the development of global cultural knowledge and allow to responding more effectively to modern challenges in the field of culture.
REFERENCES
1. Zhu B, Ma R, Luo M, Wu L, Fu W. An Identification Method of the Externality of Cultural Facilities from the Perspective of Spatial Distribution of Cultural Industry: A Case Study of Ningbo, China. Buildings [Internet] 2023;13(3). Available in: https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030692
2. Eshak ES, Baba S, Yatsuya H, Iso H, Hirakawa Y, Mahfouz EM, El-Khateeb AS. Work and Family Conflicts, Depression, and “Ikigai”: A Mediation Analysis in a Cross-cultural Study Between Japanese and Egyptian Civil Workers. Journal of Epidemiology [Internet] 2023;33(7):360–366. Available in: https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20210338
3. Falkof N. Cultural studies in South Africa, or not. International Journal of Cultural Studies [Internet] 2023;26(1):16-21. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1177/13678779221131346
4. Rentzou K, Slutsky R, Gol-Guven M, Kragh-Müller G, Tuul M, Paz-Albo J. A Cross-Cultural Study on Factors Affecting Children’s Agentic Action in Their Play. International Journal of Early Childhood [Internet] 2023;55(1):89-112. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13158-022-00335-w
5. Szulc Ł. Culture is transnational. International Journal of Cultural Studies [Internet] 2023;26(1):3-15. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1177/13678779221131349
6. Matthews MR. Cultural studies in science education: A philosophical appraisal. Cultures of Science [Internet] 2023;6(2):199-213. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1177/20966083231173721
7. Parayil SK. Media and Cultural Studies. In Practicing Interdisciplinarity [Internet] 2023;186–197. Routledge India. Available in: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003329428-13
8. Gullotta D, Lin L. Grass Stage as a Method: (Un)Doing Cultural Studies in China. Notebooks: The Journal for Studies on Power [Internet] 2023;2(1):54-79. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1163/26667185-bja10027
9. Pope K, Hewlin-Vita H, Chu EMY. The Human Library and the development of cultural awareness and sensitivity in occupational therapy students: a mixed methods study. Frontiers in Medicine [Internet] 2023;10. Available in: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1215464
10. Teoh MW, Kwek A, Wang Y. An analytical autoethnographic study of culture’s role in transformative tourism experiences. Tourism Management Perspectives [Internet] 2023;46. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2023.101097
11. Dos Santos CA. Fighting disinformation and the subject’s social protagonism: interrelation between Stuart Hall’s Cultural Studies and Media and Information Literacy. Encontros Bibli [Internet] 2023;28(Special). Available in: https://doi.org/10.5007/1518-2924.2023.e92988
12. Koumoutsea A, Boufounou P, Mergos G. Evaluating the Creative Economy Applying the Contingent Valuation Method: A Case Study on the Greek Cultural Heritage Festival. Sustainability [Internet] 2023;15(23):16441. Available in: https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316441
13. Skaria R, Montayre J. Cultural intelligence and intercultural effectiveness among nurse educators: A mixed-method study. Nurse Education Today [Internet] 2023;121. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105714
14. Mukhalalati B, Ahmed A, Elshami S, Awaisu A. Cultural Competence among Healthcare Professional Educators: A Mixed-Methods Study. Sustainability (Switzerland) [Internet] 2023;15(18). Available in: https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813793
15. Arya A. An Overview of Textual Analysis as a Research Method for Cultural Studies. International Journal for Innovative Research in Multidisciplinary Studies [Internet] 2020;6(3):173–177. Available in: https://www.ijirmf.com/wp-content/uploads/IJIRMF202003030.pdf
16. Pashkevych M, Shyber O, Kozlovska M, Semykras V, Kabanets O, Korolenko I. The trends of the cultural studies development in the modern conditions: the case of Ukraine. Multidisciplinary Science Journal [Internet] 2023; Malque Publishing. Available in: https://doi.org/10.31893/multiscience.2023ss0516
17. Gibson M. From broadcast media to distributed systems–John Hartley’s ‘cultural science’ and the future of ‘old’ cultural studies. Continuum [Internet] 2023;37(3), 313-328. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1080/10304312.2023.2250937
18. Cabalquinto E. The Paradox of a Mobile Society: Situating Cultural Studies in the Global South Context. International Journal of Cultural Studies [Internet] 2023;26(1):22–33. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1177/13678779221134308
19. Searight HR. The Value of Qualitative Methods in Cross Cultural Education: A Case Study from a First Person Perspective. International Journal of Methodology [Internet] 2023;2(1):28-33. Available in: https://doi.org/10.21467/ijm.2.1.6139
20. Ali M, Uddin Z, Banik PC, Hegazy FA, Zaman S, Ambia ASM, Ahsan GU. Knowledge, Attitude, Practice, and Fear of COVID-19: an Online-Based Cross-cultural Study. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction [Internet] 2023;21(2):1025–1040. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-021-00638-4
FINANCING
The authors did not receive financing for the development of this research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Data curation: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Formal analysis: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Research: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Methodology: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr
Project management: Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Resources: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Software: Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Supervision: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Validation: Olena Hubernator, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Display: Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.
Drafting - original draft: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Iryna Shvets.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Liudmyla Polishchuk, Olena Hubernator, Iryna Shvets, Volodymyr Pylypiv, Kabanets Oleksandr.