Category: Finance, Business, Management, Economics and Accounting
ORIGINAL
Operational excellence (OpEx) through entrepreneur’s strategic business decision making and emotional contagion in the service industry
Excelencia operativa (OpEx) a través de la toma de decisiones empresariales estratégicas del empresario y el contagio emocional en el sector servicios
Marirajan Murugan1 ![]() *, M.N. Prabadevi1
*, M.N. Prabadevi1 ![]() *
*
1Faculty of Management, Vadapalani Campus, SRM IST, India.
Cite as: Murugan M, Prabadevi M. Operational excellence (OpEx) through entrepreneur’s strategic business decision making and emotional contagion in the service industry. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias. 2024; 3:902. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2024902
Submitted: 06-02-2024 Revised: 24-04-2024 Accepted: 12-06-2024 Published: 13-06-2024
Editor: Dr.
William Castillo-González ![]()
ABSTRACT
Petroleum products play a critical role in the global industry. India is the third most significant crude oil importer in the world, of which 22 % from Russia in October 2022. Emotional Contagion refers to an entrepreneur influencing the emotions and behaviours of another entrepreneur and employees in the company to achieve operational excellence. Entrepreneurs’ decision-making styles vary from analytical, conceptual, directional, and behavioural to attain the corporate goal. The utilitarian theory states that entrepreneurs, as utilitarians, lead the company with a highly ethical, moral, good environment & culture and, at the same time, target for the company’s profit. We have considered twenty five companies from India and the Middle East region to study Entrepreneur’s strategic business decision styles and emotional Contagion. We have used a Stratified sampling technique to collect data. We have used JAMOVI for the data analysis. This paper examines entrepreneurs’ strategic business decision styles and emotional Contagion toward Utilitarianism in the Oil and Gas service industry. It provides positive and negative effects for which we have recommended that the government and MSMEs must focus on providing psychological training to entrepreneurs to achieve the highest positive emotional contagion, safe and healthy organizational culture positively.
Keywords: Operational Excellence; Entrepreneur; Strategic Business Decision Making; Organizational Culture; Emotional Contagion; Service Industry.
RESUMEN
Los productos petrolíferos desempeñan un papel fundamental en la industria mundial. India es el tercer importador de crudo más importante del mundo, de los cuales el 22 % procedía de Rusia en octubre de 2022. El contagio emocional hace referencia a un empresario que influye en las emociones y comportamientos de otro empresario y de los empleados de la empresa para alcanzar la excelencia operativa. Los estilos de toma de decisiones de los empresarios varían entre analítico, conceptual, direccional y conductual para alcanzar el objetivo empresarial. La teoría utilitarista afirma que los empresarios, como utilitaristas, dirigen la empresa con un entorno y una cultura altamente éticos, morales y buenos y, al mismo tiempo, tienen como objetivo el beneficio de la empresa. Hemos considerado veinticinco empresas de la India y de la región de Oriente Medio para estudiar los estilos de decisión empresarial estratégica de los empresarios y el contagio emocional. Hemos utilizado una técnica de muestreo estratificado para recoger los datos. Hemos utilizado JAMOVI para el análisis de datos. Este artículo examina los estilos de decisión empresarial estratégica de los empresarios y el contagio emocional hacia el utilitarismo en la industria de servicios del petróleo y el gas. Proporciona efectos positivos y negativos por lo que hemos recomendado que el gobierno y las MIPYMES deben centrarse en proporcionar formación psicológica a los empresarios para lograr el mayor contagio emocional positivo, seguro y saludable positivamente la cultura organizacional.
Palabras clave: Excelencia Operativa; Empresario; Toma de Decisiones Estratégicas Empresariales; Cultura Organizacional; Contagio Emocional; Industria de Servicios.
INTRODUCTION
By utilizing the extensive research findings from the last 25 years, researchers examined the concept of emotional contagion in the context of organizations. They provided a definition of emotional contagion, explored methods to measure this phenomenon, and discussed individual characteristics that affect the likelihood of being influenced by emotional contagion.(28) The behavior of leaders has a direct impact on the trust and contentment of employees within the organization, hence strengthening the relationship between leadership and organizational effectiveness.(21) Emotions have the ability to propagate among individuals, which is referred to as emotion contagion. Both happy and negative emotions are considered to be contagious, however, the widespread transmission of negative emotions has garnered the greatest attention due to its perilous impact on society.(23) There is a growing interest in incorporating emotions into economic management. Personal emotion, being a crucial irrational factor, frequently exerts a substantial influence on business decision-making processes. Researchers discovered that, apart from entrepreneurs, employees experience unpleasant emotions after the consideration of entrepreneurial failure is also necessary, as they contended that it is important to cultivate an organizational climate. Leaders should provide assistance to employees who experience negative emotions as a result of failure. Additionally, research has shown that supportive leaders can assist employees in reducing negative emotions following entrepreneurial failure, leading to enhanced job satisfaction and performance.(27)
Furthermore, a well-structured questionnaire (Refer Appendix-1) and interviews were conducted to collect the responses from twenty five respondents from MSME entrepreneurs from Middle East and India region. Researchers used stratified sampling to collect the data from respondents. The statistical tool used in this study is JAMOVI, and data was analyzed through descriptive statistics, Reliability analysis, correlation and multiple regressions. Researchers observed that the variation in the organizational operational excellence through Entrepreneur’s business strategy, decision making, organizational culture and emotional contagion. Researchers observed that entrepreneur’s organizational culture and positive emotional contagion can maximize their Organization’s operational excellence by utilizing and sustaining the proposed model in the service industry. Government and MSMEs have to update their policies to have periodical audit and provide psychological training to comply healthy organizational culture and entrepreneur’s positive emotional contagion in service industry.(20) Future research can be explored to study the entrepreneurs across the world.
Literature review
Service Industry
The energy service industry encompasses various sectors, including oil and gas (upstream, midstream, and downstream), renewable energy, Power, metals and minerals, pipelines, offsites and utilities. Plants can be classified into two categories(15): green field plants, which are newly planted, and brown field plants, which are either revamped or modified from existing plants. Small service businesses are facing challenges due to rising operating expenses, which are being compelled by market competition to increase their operating costs in order to maintain competitiveness. Both public and commercial entities are significantly contributing to the Indian Oil & Gas sector. The leading public sector organizations in the industry include IOC, ONGC, HPCL, BPCL, OIL, and GAIL. On the other hand, the leading private sector firms in the industry include RIL, Essar Oil Limited, Adani Gas, Petronet LNG, Cairn, Shell, Middle east region service providers, BG Group, BP and international joint venture service providers. The industry participants primarily engage in a wide array of activities, encompassing exploration, production, refining, marketing, infrastructure, and various multi-sector operations. The incumbent service providers have been intensifying their competitiveness by expanding their operations and capacities, increasing their fleet size, diversifying their portfolio by offering specialized services, and improving their workforce. Several local companies are also intending to provide their services to oil and gas companies worldwide. Indian refineries are currently prioritizing horizontal integration as a strategic approach to expand their operations and diversify their product portfolio, hence generating supplementary revenue streams.
Entrepreneur’s Emotional Contagion
Emotional contagion is the transmission of one person’s behaviors and emotions to another one.(16,17) Emotional contagion mechanisms have a significant impact on various organizational and leadership outcomes.(5) Behavioral responses can serve as a means of transmitting emotions to others. These reactions can be communicated either verbally or in writing format, such as by favorable or negative consumer reviews on online forums.(7) The impact of a leader’s positive and negative emotions in the workplace on a follower’s positive emotions at work is connected through emotional contagion.(12) One field study and one experiment offer empirical evidence for a contagion effect of entrepreneurial passion and demonstrate the specific effects of entrepreneurs’ enthusiasm on employee outcomes.(8) Emotional contagion and emotional regulation are two areas that could particularly benefit from employing a neuroscientific approach.(19) The study investigated the phenomenon of group emotional contagion, which refers to the spread of emotions inside a group, and its impact on the dynamics of work groups. This was done through a laboratory experiment that measured mood, individual attitudes, behavior, and group-level dynamics using numerous, convergent methods.(2,3) Emotions exhibited within an entrepreneurial organization have the capacity to spread to other stakeholders, such as employees.(29) Emotional contagion has a dual effect on the company: it affects the internal mechanisms involved in managing emotions to address various issues within the organization, and it enables employees to engage in necessary social processes, potentially impacting nearly every aspect of the company. Emotional contagion facilitates the ability to control and manage emotions when confronted with intense emotions, such as uncertainty. Consequently, the cultivation of self-control is expected to yield a more equitable and rational approach towards the challenges encountered in the business, encompassing decision-making and social interactions, thereby enhancing overall performance. It is imperative for employees to regulate their own emotions while assessing and exerting influence on the emotions of others, as this can greatly affect the overall performance of the firm. This is crucial since employee behavior is fundamentally influenced by emotions and can greatly affect all aspects of employee performance, company outcomes, and client relationships. Consequently, emotional contagion facilitates the cultivation of employee potential and the establishment of a pathway to long-term performance and achievement. The influence of information contagion is powerful enough to result in the market being dominated by one of the competing services. The specific service that achieves dominance may be influenced by random sampling variations and cannot be predicted in advance.(25) Identifying and activating specific neural populations in the brain that are responsible for observing the distress of others, and then assessing their involvement in self-preservation or other-regarding behaviors, could lead to a more detailed understanding of how these two motives interact and balance each other. Additionally, this approach may provide insights into individual differences that are relevant to psychiatric disorders. The next frontier may lie in determining where in the brain human emotional contagion is utilized to enlist others as sentinels or to provide them with advantages.(30) Leaders, Managers and supervisors have a crucial role in facilitating the effective and seamless implementation of teamwork involvement in the workplace, going beyond just striving to maximize its overall levels.(22) The significance of emotional contagion in relation to company performance lies in its impact on an individual’s inclination to engage in a startup and their propensity to undertake risky endeavors in quest of such opportunities. In order to effectively convince prospective investors and partners to endorse their endeavors and secure the essential resources and skills necessary for long-term viability, it is imperative for an employee to possess the capacity to identify and regulate the emotions of others. Social engagement necessitates the presence of self-control and impulse control. Self-regulation and impulse control encompass the management of personal goals, the formulation of strategies to attain those goals, and the handling of challenges that may arise, including one’s emotional response. Emotional intelligence exerts a significant influence on interpersonal dynamics and a diverse range of social competencies that are important to an individual’s professional achievements. Nevertheless, the achievement of these individuals in the economic realm has lately been attributed to their cognitive abilities and social intelligence aptitudes. Accurately perceiving others, creating a favorable initial impression, and effectively persuading or influencing others in interpersonal interactions are among the various abilities involved.
Entrepreneur’s Strategic Business Decision Making
Emotion has been a black box in strategic decision making. The decision maker’s emotional experience plays a role in promoting cognitive simplification behaviour. This occurs through the connection between cognition and affect in mental functioning, ultimately resulting in a decrease in the decision maker’s decision comprehensiveness.(14)
The decision-making styles encompass four distinct approaches, namely Analytical, Directive, Conceptual, and Behavioural. The decision-making style framework is formed via the collaboration of two spectrums. The first continuum pertains to the inclination towards either structure, characterized by well-defined processes and expectations, or ambiguity, characterized by open-ended and flexible approaches. There is a distinction between the task/technical and people/social spectrum. This spectrum assesses whether the decision-making process is primarily driven by a desire for correctness or achieving outcomes (task/technical), or if it is motivated by the goal of fostering harmony or making a social effect (people/social). Analytical style decision making refers to those who exhibit a propensity for embracing ambiguity while maintaining a strong drive to identify the optimal or most comprehensive solution. If entrepreneur possess an analytical decision-making style, it is probable that entrepreneur require a significant amount of time to deliberate about significant life choices. The individual’s level of comfort with ambiguity does not necessarily indicate a propensity for risk-taking or a propensity to make decisions without prior knowledge. Conversely, entrepreneur’s inclination towards ambiguity indicates that entrepreneur derive pleasure from thoroughly evaluating all possibilities prior to reaching a conclusion. Entrepreneur possess the ability to generate innovative ideas and are open to granting each potential opportunity. Nevertheless, entrepreneur want to proceed only when entrepreneur are highly confident that that decision is optimal. Analytical type decision-makers excel at making responsible decisions, but they struggle with making timely decisions, effectively communicating with others, and managing stress during the decision-making process. The concept of directive style decision making pertains to those that exhibit a need for organization and are driven by If entrepreneur possess a directive style decision-making approach, it is probable that entrepreneur make decisions expeditiously and adopt a mindset of “decide and move forward.” Entrepreneur have a preference for taking action rather than lingering on possibilities. In order to expedite decision-making, entrepreneur often depend on case studies and guidelines as a guide to guide your actions. The notion of “reinventing the wheel” is perceived as a futile endeavour, a perspective that extends to one’s individual decision-making processes. Entrepreneur communication skills are one of your prominent strengths. Entrepreneur decisions exude confidence, purpose, and a tangible feeling of concreteness, which is highly admired by others. This self-assurance enables entrepreneur to get backing and confidence for the decisions entrepreneur make. Nevertheless, decision-makers who adopt a dictatorial approach often encounter difficulties when it comes to receiving advice, addressing divergent viewpoints, and formulating strategies in novel or ambiguous circumstances. Conceptual style decision making refers to those that derive satisfaction from the uncertainty of open-ended choices and are driven to have a significant influence on the world. If entrepreneur possess a conceptual style decision-making approach, it is probable that entrepreneur engages in frequent daydreaming and promptly generates innovative thoughts when required. One may observe the interconnectedness and mutual influence of most things. Entrepreneurs aspire to design comprehensive solutions. Entrepreneur’s adeptness in navigating ambiguity enables entrepreneur to engage in expansive thinking and cultivate a greater sense of optimism regarding the success of entrepreneur’s ideas, surpassing individuals with alternative decision-making approaches. Entrepreneur’s areas of expertise lie in identifying fundamental issues and devising innovative, cohesive strategies to pursue. However, many decision-makers who adopt a conceptual style often struggle with making decisions and ensuring their implementation. The behavioural style of decision making pertains to individuals who exhibit a preference for rigidity and stability, driven by a motivation to uphold harmony. If one identifies as a behavioural style decision maker, it is likely that their relationships have significant importance in their lives. Research suggests that individuals often prioritize the needs and opinions of their family, friends, and colleagues over their own. The task of reconciling the need for organization with the consideration of others’ perspectives and emotions may appear challenging. However, decision-makers who adopt a behavioural style achieve this by actively soliciting information and assessing They utilize the collected knowledge to devise solutions that they anticipate would be well-received by others, and often seek counsel prior to proceeding with a decision. One of the notable strengths exhibited by decision-makers with a behavioural style is their capacity to foster a sense of inclusion and importance among others, so obtaining their support and effectively expressing their conclusions. Nevertheless, their vulnerabilities lie in their lack of self-confidence and their struggle to navigate conflicts. Decision-makers who adopt a behavioural style may be susceptible to being influenced by the advice and opinions of others. They might be referred to as “compliant individuals.” They find it difficult to handle conflict. In order to evade it, people occasionally assume superfluous levels of responsibility and stress.
Emotion regulation might result in unforeseen and adverse consequences for strategic actors who appear insincere. Conversely, strategic individuals who genuinely display their feelings can foster dedication and minimize emotional unrest at all levels within a business.(4) Emotions are powerful, widespread, predictable, and can occasionally have negative or positive effects on decision making. Emotions have a consistent impact on judgment and choice, regardless of the sort of decision being made. Therefore, emotional reactions are neither haphazard nor secondary phenomena.(11) Behaviour in companies is influenced by various emotional and implicit elements. The use of neuroscience approaches can aid in understanding these processes and developing strategies that optimize brain function to achieve desired objectives.(18) Preventive control measures primarily focus on persons who are susceptible, while treatment control strategies primarily target individuals who are infected.(26)
Organizations Operational Excellence
OpEx provides design standards and recommendations that facilitate organic business growth by redirecting management’s focus from operational tasks to business expansion.(13) Companies employ several components of multiple management systems and concepts concurrently. These management systems offer essential insights for achieving Operational Excellence.(6) The influence of leaders on the emotional environment and culture of their teams and organizations is substantial. By demonstrating and advocating for emotional behaviors and norms that align with the company vision and values, they can foster a positive work culture through emotional contagion. This encompasses the demonstration of genuine and suitable emotions that serve as sources of motivation for team members, the identification and acknowledgement of their feelings and requirements, the promotion of emotional expression and interchange, and the provision of rewards for emotional accomplishments and contributions. In addition, leaders should offer their team members emotional assistance, direction, and resources, while also establishing a secure and courteous environment for constructive criticism and resolving conflicts. Teams may optimize their performance and well-being by cultivating and sustaining strong and healthy emotional connections and interactions with their leaders and peers, thereby harnessing the power of emotional contagion. To achieve this, individuals should cultivate mindfulness and respect for their own and others’ emotions, while actively avoiding the transmission of negative emotions, such as pessimism, anger, fear, and resentment, which can negatively impact their performance and overall well-being. In addition, teams should engage in effective and efficient communication and collaboration with their team members, utilizing emotional cues and feedback to synchronize their objectives, expectations, and behaviours. Moreover, it is imperative for teams to actively pursue and provide emotional support and aid to their team members, while also managing stress and overcoming problems collectively. Ultimately, teams need to acquire and develop from their emotional encounters and criticism, utilizing them to enhance their abilities, expertise, and mindsets. According to A.M. Carvalho, operational excellence can be achieved through the inseparable connection between culture and excellence, the impact of culture on the creation of strategies and the impact of strategies on the development of culture, the recurring patterns in the relationships between excellence, culture, and strategy, and the cause and effect relationships between the implementation of factors that enable excellence and the development of factors that enable agility and capabilities.(1) Consistent with the previous rationale regarding perceived supervisor support and perceived co-worker support, we hypothesize that when employees perceive a high level of organizational support, the detrimental effect of surface acting on job performance will be mitigated, while the beneficial effect of deep acting on job performance will be enhanced.(10)
Research Problem
Organizational culture and Emotional contagion’s tipping point between positive and negative(20) need to have further developments and improvement in this service industry and myriad effects in organizational life. We observed that we will have to improve existing model with service industry operational excellence through entrepreneurs business strategy, decision making, organizational culture and emotional contagion.
Research Gap
The impact of emotions and the study of how to effectively control these shared feelings, in order to minimize their negative consequences and enhance their influence on desired strategic results, is still in its early stages of development.(9) Entrepreneur’s business strategy, decision making, organizational culture, emotional contagion and organizational operational excellence were not studied before to meet organizational targets to meet positive way and healthy organizational work life balance. We found the research gaps in earlier studies and to overcome these gaps in middle east and Indian region service industry, for which researchers have explored further to meet the above criteria.
METHOD
Researchers used descriptive research studies for the research. Researchers prepared a well-structured questionnaire (Refer Appendix-1), and interviews were conducted to collect the data from twenty five respondents from MSME entrepreneurs. Researchers used stratified sampling to collect the data from respondents.
The statistical tool used in this study is JAMOVI and analyzed the data through descriptive statistics, Reliability analysis and correlation and multiple regressions.
This research paper aims to shed light on organizations operational excellence in the service industry through entrepreneurs business strategy, decision making, emotional contagion and organizational culture.(24) Figure 1 shows the proposed model for the organizations operational excellence.
The literature review identified twenty-five variables with the organizational, operational excellence and MSME organization’s operational excellence through entrepreneurs business strategy, decision making, emotional contagion and organizational culture. Detailed reviews and in-depth interviews were conducted for the derived variables. The following hypothesis was developed based on the earlier researchers described in section 7.0.
H1: Entrepreneurs business strategy, decision making, organizational culture are positively associated with entrepreneur’s emotional contagion.
H2: Entrepreneurs business strategy, decision making, organizational culture, entrepreneur’s emotional contagion are negatively associated with organization’s operational excellence.
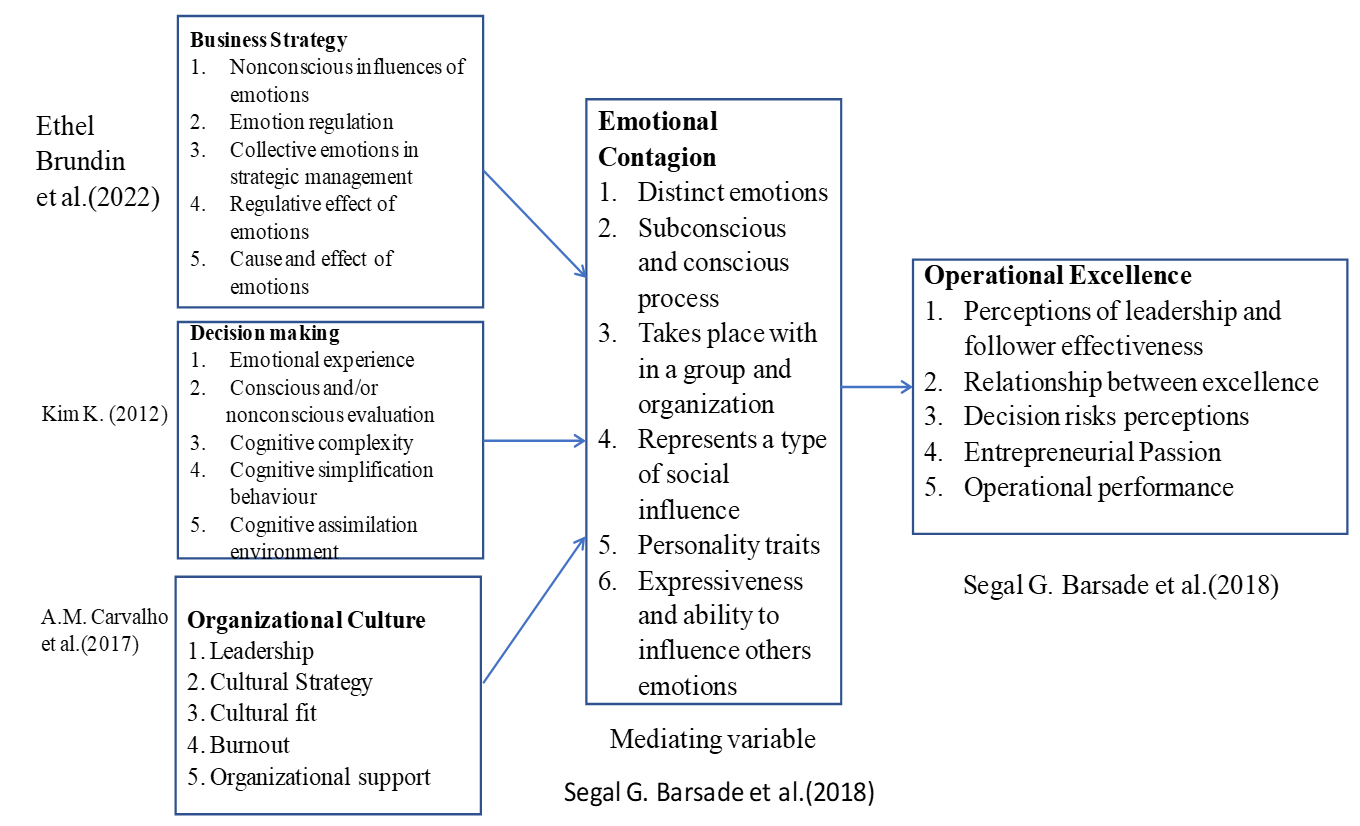
Figure 1. Proposed model for operational excellence (Op Ex) through entrepreneur’s strategy business decision making and emotional contagion in the service industry
RESULTS
Data was analyzed through JAMOVI. MSME entrepreneur’s statistics are given below. Socio-demographic details of the respondents shown in table 1.
|
Table 1. Socio-demographic details of the respondents – (n=25), Frequency Statistics – MSME Entrepreneurs. |
|||
|
Statistics |
Age |
Gender |
|
|
N |
Valid |
25 |
25 |
|
Missing |
0 |
0 |
|
While applying Likert’s scale in the study, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is necessary to evaluate consistency and reliability (Joseph et.al., 2003). Table 2 provides Cronbach’s Alpha against each factor considered in the study.
Reliability Analysis
|
Table 2. Consistency and Reliability Analysis |
|
|
Scale Reliability Statistics |
|
|
Cronbach’s α |
|
|
Scale |
0,803 |
Table 2 shows consistency and reliability achieved against each factor and it proves the high level internal consistency for the scale.
Karl Pearson Correlation
The table 3 below shows that Business strategy, Decision making, Organizational culture and Emotional contagion are positively correlated. Operational excellence is negatively correlated with Business strategy, Decision making, Organizational culture and Emotional contagion.
The colours of each cell represents the strength and direction of the correlation, with darker colours indicating stronger correlations. Positive correlation is stronger between Business strategy, Decision making and Emotional contagion. Positive correlation is negligible between organizational culture and emotional contagion. Negative correlation is stronger between operational excellence and organizational culture and emotional contagion. Negative correlation is negligible between operational excellence and business strategy and decision making. Correlation between entrepreneur’s business strategies shown in figure 2.
Correlation Heatmap

Figure 2. Correlation between entrepreneur’s business strategies, entrepreneur’s decision making, organizational culture, entrepreneur’s emotional contagion and organization’s operational excellence
Correlation Matrix
|
Table 3. Correlation between Entrepreneur’s business strategy, Entrepreneur’s Decision making, Organizational culture, Entrepreneur’s emotional contagion and Organization’s operational excellence |
||||||
|
Correlation Matrix |
||||||
|
|
|
OE_TOT |
EC_TOT |
OC_TOT |
DM_TOT |
BS_TOT |
|
OE_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
df |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
p-value |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
EC_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,719 |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
df |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
p-value |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
|
|
OC_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,608 |
0,796 |
— |
|
|
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
|
p-value |
0,001 |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
|
DM_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,298 |
0,717 |
0,690 |
— |
|
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
p-value |
0,149 |
< ,001 |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
BS_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,262 |
0,612 |
0,633 |
0,970 |
— |
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
p-value |
0,206 |
0,001 |
< ,001 |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
||||||
Correlation Matrix
|
Table 4. Positive correlation between Entrepreneur’s business strategy, Entrepreneur’s Decision making, Organizational culture, Entrepreneur’s emotional contagion and Organization’s operational excellence |
||||||
|
Correlation Matrix |
||||||
|
|
|
OE_TOT |
EC_TOT |
OC_TOT |
DM_TOT |
BS_TOT |
|
OE_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
df |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
p-value |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
EC_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,719 |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
df |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
p-value |
1,000 |
— |
|
|
|
|
OC_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,608 |
0,796 |
— |
|
|
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
|
p-value |
0,999 |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
|
DM_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,298 |
0,717 |
0,690 |
— |
|
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
p-value |
0,926 |
< ,001 |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
BS_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,262 |
0,612 |
0,633 |
0,970 |
— |
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
p-value |
0,897 |
< ,001 |
< ,001 |
< ,001 |
— |
|
Note. Ha is positive correlation |
||||||
Correlation Matrix
|
Table 5. Negative Positive correlation between Entrepreneur’s business strategy, Entrepreneur’s Decision making, Organizational culture, Entrepreneur’s emotional contagion and Organization’s operational excellence |
||||||
|
Correlation Matrix |
||||||
|
|
|
OE_TOT |
EC_TOT |
OC_TOT |
DM_TOT |
BS_TOT |
|
OE_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
df |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
p-value |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
EC_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,719 |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
df |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
p-value |
< ,001 |
— |
|
|
|
|
OC_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,608 |
0,796 |
— |
|
|
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
|
p-value |
< ,001 |
1,000 |
— |
|
|
|
DM_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,298 |
0,717 |
0,690 |
— |
|
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
|
p-value |
0,074 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
— |
|
|
BS_TOT |
Pearson’s r |
-0,262 |
0,612 |
0,633 |
0,970 |
— |
|
|
df |
23 |
23 |
23 |
23 |
— |
|
|
p-value |
0,103 |
0,999 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
— |
|
Note. Ha is negative correlation |
||||||
Positive correlation between Entrepreneur’s business strategy shown in table 4. Negative Positive correlation between Entrepreneur’s business strategy shown in table 5. Furthermore, the correlation values are found to be significant. The correlation coefficient between business strategy and decision making is 0,97 (0,972 = 0,94), with 94 % positive relationships between business strategy and decision making. The correlation coefficient between an Organization’s culture and an Emotional Contagion is 0,8 (0,82 = 0,64), with 64 % positive relationships between Organization’s culture and an Emotional Contagion. The correlation coefficient between emotional contagion and operational excellence is 0,72 (0,722 = 0,52), with 52 % negative relationships between emotional contagion and operational excellence. The correlation coefficient between organizational culture and operational excellence is 0,61 (0,612 = 0,37), with 37 % percentage negative relationships between organizational culture and operational excellence.
Regression Analysis
Independent Variables: Business strategy, Decision making, Organizational culture and Emotional contagion.
Dependent Variable: Operational excellence.
|
Table 6. Linear Regression |
||||
|
Model Fit Measures |
||||
|
Model |
R |
R² |
Adjusted R² |
RMSE |
|
1 |
0,842 |
0,709 |
0,651 |
0,175 |
The above table 6 shows the regression analysis of the organizations operational excellence. The table shows that the regression values are significant and the model perfectly fits. The multiple correlation coefficient is 0,842, which indicates the highest relationship of the operational excellence. Linear combination of business strategy, decision making, organizational culture, emotional contagion and operational excellence and the coefficient value of 0,842 indicates that the relationship between the operational excellence and the four independent variables is quite solid and positive. The value of R square is 0,709, meaning that about 70,1 % of the variation in the Entrepreneur’s performance is explained by the estimated SRP impacted by entrepreneurs operational excellence, business strategy, decision making, organizations culture and emotional contagion.
CONCLUSIONS
Researchers scrutinized the organizational operational excellence and found that organizational culture and entrepreneur’s emotional contagion need to be improved. Entrepreneur’s emotional contagion has positively and negatively impacted with organizational operational excellence. Organizational operational excellence has negatively correlated with entrepreneur’s business strategy, decision making and emotional contagion and organizational culture. Researchers observed that organizational culture and entrepreneur’s emotional contagion still need to be fully matured for organizational operational excellence and employees healthy work life balance. Researchers concluded that the variation in the organizational operational excellence through Entrepreneur’s business strategy, decision making, organizational culture and emotional contagion. Researchers concluded that entrepreneurs organizational culture and positive emotional contagion can maximize their Organization’s operational excellence by utilizing and sustaining the proposed model in the service industry.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Entrepreneur’s organizational culture and positive emotional contagion must be trained, developed and implemented to meet the organizational operational excellence to meet the target budget of capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operational expenditure (OPEX) of MSME entrepreneurs and employees work life balance to have positive harmony in the organization. The government and MSMEs must focus on providing psychological training to entrepreneurs to achieve the highest positive emotional contagion and healthy organizational culture positively. Government and MSMEs have to update their policies to have periodical audit and provide psychological training to comply healthy organizational culture and entrepreneur’s positive emotional contagion in service industry. Future research can be explored to study the entrepreneurs across the world.
REFERENCES
1. Carvalho AM, Sampaio P, Rebentisch E, Saraiva P. Operational excellence as a means to achieve an enduring capacity to change–revision and evolution of a conceptual model. Procedia Manufacturing. 2017 Jan 1; 13: 1328-1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.109
2. Barsade SG. The ripple effect: Emotional contagion and its influence on group behavior. Administrative science quarterly. 2002 Dec; 47(4): 644-675. https://doi.org/10.2307/3094912
3. Sotnikova O, Zhidko E, Prokshits E, Zolotukhina I. Administration of Sustainable Development of Territories as One of the Approaches for Creating A Biosphere-Compatible and Comfortable Urban Environment. Arhiv za tehničke nauke, 2022; 1(26): 79–90.
4. Ethel B. Emotion in strategic management: A review and future research agenda, Long Range Planning. 2022; 55(4): 102144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2021.102144
5. Eugene YJT. The emotional link: Leadership and the role of implicit and explicit emotional contagion processes across multiple organizational levels. The Leadership Quarterly. 2015; 26(4): 654-670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2015.05.009
6. Felsberger A, Oberegger B, Reisinger S, Reiner G. Decision Support for Operational Excellence in Manufacturing Systems. International Conference on Knowledge Technologies and Data-Driven Business 2017 (i-Know 2017). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2025
7. Herrando C, Constantinides E. Emotional contagion: A brief overview and future directions. Frontiers in psychology. 2021 Jul 16; 12: 712606. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.712606
8. Hubner S, Baum M, Frese M. Contagion of entrepreneurial passion: Effects on employee outcomes. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice. 2020 Nov; 44(6): 1112-1140. https://doi.org/10.1177/1042258719883995
9. Huy QN. Emotions in strategic organization: Opportunities for impactful research. Strategic Organization. 2012 Aug; 10(3): 240-247. https://doi.org/10.1177/1476127012453107
10.Kim HJ, Hur WM, Moon TW, Jun JK. Is all support equal? The moderating effects of supervisor, coworker, and organizational support on the link between emotional labor and job performance. BRQ Business Research Quarterly. 2017 Apr; 20(2): 124-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brq.2016.11.002
11.Lerner JS, Li Y, Valdesolo P, Kassam KS. Emotion and decision making. Annual review of psychology. 2015 Jan 3; 66: 799-823.
12.Johnson SK. I second that emotion: Effects of emotional contagion and affect at work on leader and follower outcomes. The Leadership Quarterly. 2008 Feb 1; 19(1): 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2007.12.001
13.Duggan KJ. Design for operational excellence: A breakthrough strategy for business growth. McGraw Hill Professional; 2011 Aug 17.
14.Kong-Hee K. Emotion and strategic decision-making behavior: Developing a theoretical model. International journal of business and social science. 2012 Jan 1; 3(1).
15.Camgözlü Y, Kutlu Y. Leaf Image Classification Based on Pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network Models. Natural and Engineering Sciences. 2023 Dec 1; 8(3): 214-232.
16.Banerjee P, Srivastava M. A review of emotional contagion: Research propositions. Journal of Management Research. 2019; 19(4): 250-266.
17.Verkholyak O, Dvoynikova A, Karpov A. A Bimodal Approach for Speech Emotion Recognition using Audio and Text. Journal of Internet Services and Information Security. 2021 Feb; 11(1): 80-96.
18.Radtke Caneppele N, Ribeiro Serra FA, Contreras Pinochet LH, Ramos Ribeiro IM. Potential and challenges for using neuroscientific tools in strategic management studies. RAUSP Management Journal. 2022 Aug 29; 57(3): 235-263. https://doi.org/10.1108/RAUSP-01-2021-0014.
19.Reina CS, Peterson SJ, Waldman DA. Neuroscience as a basis for understanding emotions and affect in organizations. In Organizational neuroscience. Emerald Group Publishing Limited. 2015 Dec 15, 213-232. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1479-357120150000007008
20.Srinadi NL, Hermawan D, Jaya AA. Advancement of banking and financial services employing artificial intelligence and the internet of things. Journal of Wireless Mobile Networks, Ubiquitous Computing, and Dependable Applications. 2023; 14(1): 106-117.
21.Tareque MA, Islam N. The Relationship between Leadership Behaviour and Firm Performance in the Ready-Made Garments Industries of Bangladesh. European Journal of Business and Management Research. 2023 Mar 1; 8(2): 1-6. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejbmr.2023.8.2.1855
22.Torrente P, Salanova M, Llorens S. Spreading engagement: On the role of similarity in the positive contagion of team work engagement. Revista de Psicología del Trabajo y de las Organizaciones. 2013 Dec 1; 29(3): 153-159. https://doi.org/10.5093/tr2013a21
23.Van Haeringen ES, Gerritsen C, Hindriks KV. Emotion contagion in agent-based simulations of crowds: a systematic review. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. 2023 Jun; 37(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10458-022-09589-z
24.Wiche HI. Computerization of Library Services in University Libraries in Nigeria: A Case Study. Indian Journal of Information Sources and Services, 2023; 13(1): 6–9.
25.Arthur WB, Lane DA. Information contagion. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics. 1993 Jun 1; 4(1): 81-104. https://doi.org/10.1016/0954-349X(93)90006-6
26.Hong X, Zhang G, Lu D. Control strategies for crowd emotional contagion coupling the virtual and physical cyberspace in emergencies. IEEE Access. 2020 Feb 24; 8: 37712-37726. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975808
27.Lu X, Xiong Y, Lv X, Shan B. Emotion in the Area of Entrepreneurship: An Analysis of Research Hotspots. Frontiers in psychology. 2022 Jun 15; 13: 922148. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.922148
28.Barsade SG, Coutifaris CG, Pillemer J. Emotional contagion in organizational life. Research in Organizational Behavior. 2018 Jan 1; 38: 137-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riob.2018.11.005
29.Cardon MS. Is passion contagious? The transference of entrepreneurial passion to employees. Human resource management review. 2008 Jun 1; 18(2): 77-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2008.04.001.
30.Keysers C, Gazzola V. Emotional contagion: Improving survival by preparing for socially sensed threats. Current Biology. 2021 Jun 7; 31(11): R728-R730.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors express their appreciation to the entrepreneurs who facilitated the acquisition of primary source data and conducted timely in-depth interviews, enabling the realization of this study.
FINANCING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Marirajan Murugan, M.N. Prabadevi.
Research: Marirajan Murugan, M.N. Prabadevi.
Writing - original draft: Marirajan Murugan, M.N. Prabadevi.
Writing - revision and editing: Marirajan Murugan, M.N. Prabadevi.
APPENDIX
Questionnaire with source reference:
SA-Strongly Agree: 5; A-Agree:4; N-Neutral:3; DA-Disagree:2; SD-Strongly Disagree:1
Business Strategy:
|
Sr. No. |
Content |
Source |
|
1 |
Nonconscious influences of emotions from entreprenerus |
Ethel Brundin et al. (2022) |
|
2 |
Entrepreneurs Emotion regulation |
Ethel Brundin et al. (2022) |
|
3 |
Collective emotions in strategic management |
Ethel Brundin et al. (2022) |
|
4 |
Regulative effect of emotions |
Ethel Brundin et al. (2022) |
|
5 |
Cause and effect of emotions between entrepreneurs and employees |
Ethel Brundin et al. (2022) |
Decision Making:
|
Sr. No. |
Content |
Source |
|
1 |
Emotional experience between entrepreneurs and emplyees |
Kim K. (2012) |
|
2 |
Conscious and/or nonconscious evaluation |
Kim K. (2012) |
|
3 |
Cognitive complexity |
Kim K. (2012) |
|
4 |
Cognitive simplification behaviour |
Kim K. (2012) |
|
5 |
Cognitive assimilation environment |
Kim K. (2012) |
Organizational Culture:
|
Sr. No. |
Content |
Source |
|
1 |
Leadership in organizational culture |
A.M. Carvalho et al. (2017) |
|
2 |
Cultural strategy in organizational culture |
A.M. Carvalho et al. (2017) |
|
3 |
Cultural fit in organizational culture |
A.M. Carvalho et al. (2017) |
|
4 |
Burnout in organizational culture |
A.M. Carvalho et al. (2017) |
|
5 |
Organizational support in organizational culture |
A.M. Carvalho et al. (2017) |
Emotional Contagion:
|
Sr. No. |
Content |
Source |
|
1 |
Distinct emotions from entrepreneurs |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
2 |
Subconscious and conscious process of entrepreneurs |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
3 |
Takes place with in a group and organization |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
4 |
Represents a type of social influence and Expressiveness and ability to influence others emotions |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
5 |
Personality traits from entrepreneurs |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
Operational Excellence:
|
Sr. No. |
Content |
Source |
|
1 |
Perceptions of leadership and follower effectiveness |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
2 |
Relationship between excellence |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
3 |
Decision risks perceptions |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
4 |
Entrepreneurial Passion |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |
|
5 |
Operational performance in the organization |
Segal G. Barsade et al. (2018) |